【摘要】缓存和分布式锁
前言 151、缓存-缓存使用-本地缓存与分布式缓存 缓存使用 为了系统性能的提升,我们一般都会将部分数据放入缓存中,加速访问。而db承担数据落盘工作。
哪些数据适合放入缓存?
即时性、数据一致性要求不高的。
访问量大且更新频率不高的数据(读多,写少)。
举例:电商类应用,商品分类,商品列表等适合缓存并加一个失效时间(根据数据更新频率来定),后台如果发布一个商品,买家需要5分钟才能看到新的商品一般还是可以接受的。
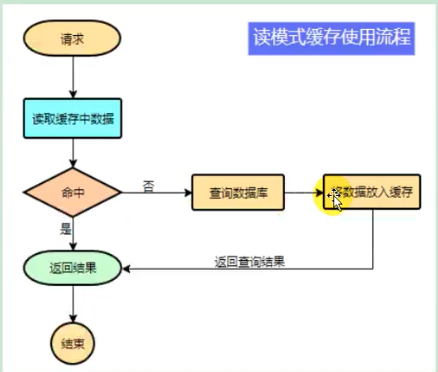
1 2 3 4 5 6 data = cache.load(id); if (data==null ){ data = db.load(id); cache.put(id,data); } return data;
注意:在开发中,凡是放入缓存中的数据我们应该指定过期时间,使其可以在系统即使没有主动更新数据也能自动触发数据加载进缓存的流程。避免业务奔溃导致我们的数据永久不一致问题。
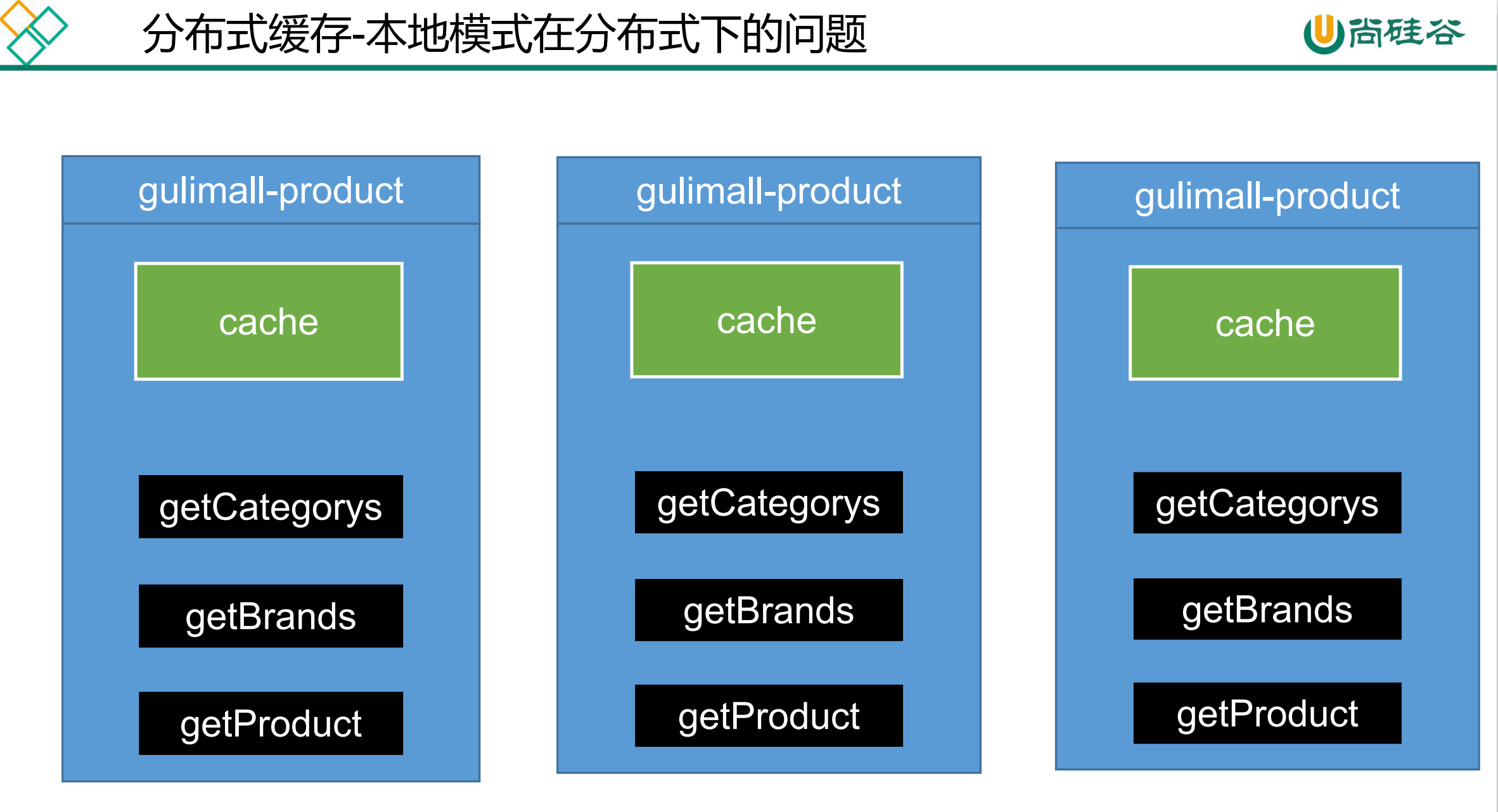
这种本地缓存每个实例都有自己的缓存,可能会出现数据不一致的情况。同时本地缓存还会占用堆内存,影响垃圾回收、影响系统性能。
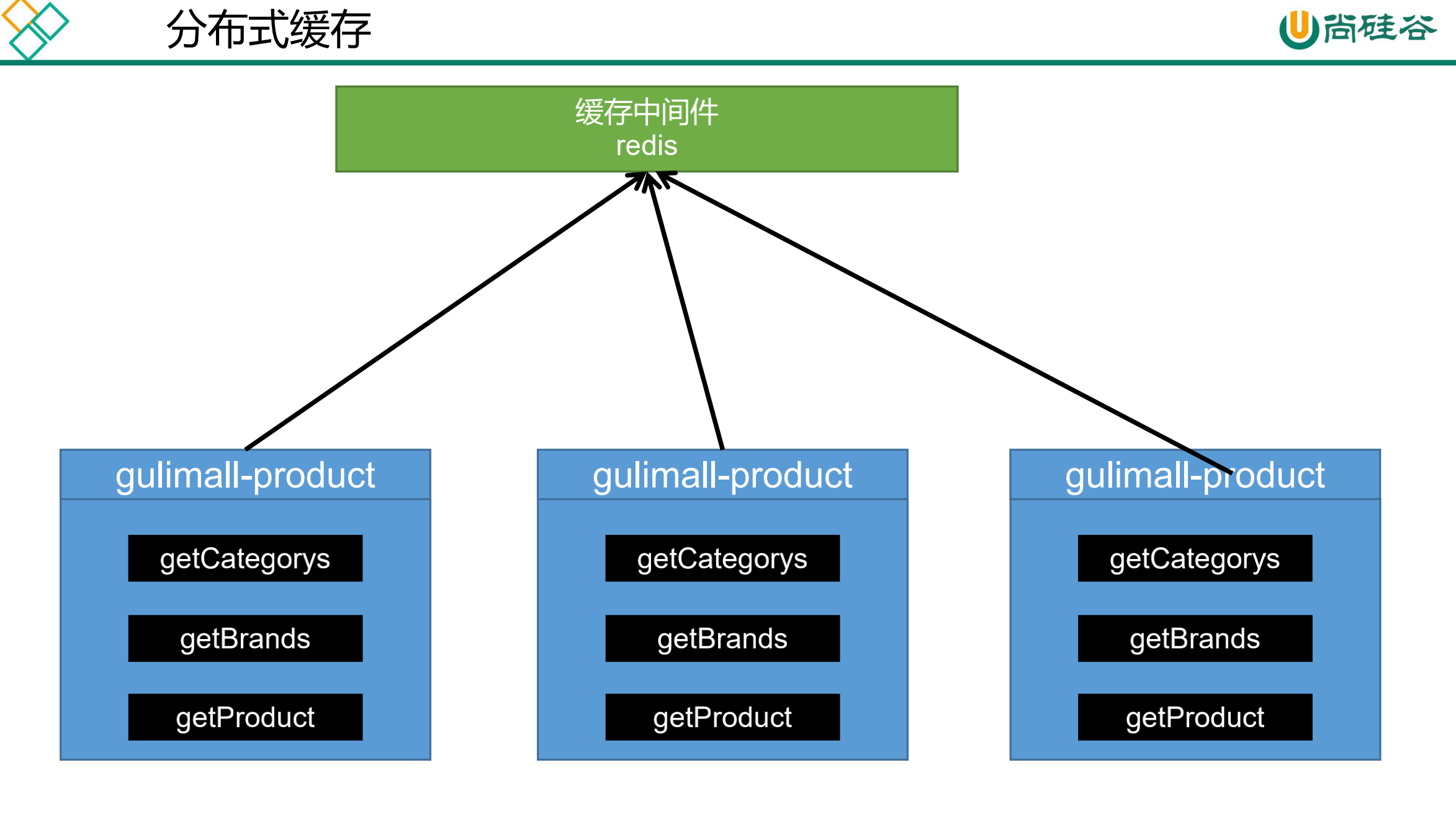
所以我们需要使用分布式缓存,不应该把缓存放在每一个微服务的进程中。常用的缓存中间件是Redis。使用缓存中间件还可以无限扩容。
152、缓存-缓存使用-整合redis测试 引入Reids。(pom.xml)
1 2 3 4 5 <!-- 引入Redis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency>
配置Redis。(application.yml)
1 2 3 4 5 spring: redis: host: 127.0 .0 .1 port: 6379 password: redis
ZheliProductApplicationTests.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Autowired private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;@Test public void testStringRedisTemplate () ValueOperations<String, String> ops = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue(); ops.set("hello" ,"world_" + UUID.randomUUID().toString()); String hello = ops.get("hello" ); System.out.println("之前保存的数据是:" +hello); }
控制台打印
1 之前保存的数据是:world_0a678d76-d227-4c10-807e-00d6320b01ce
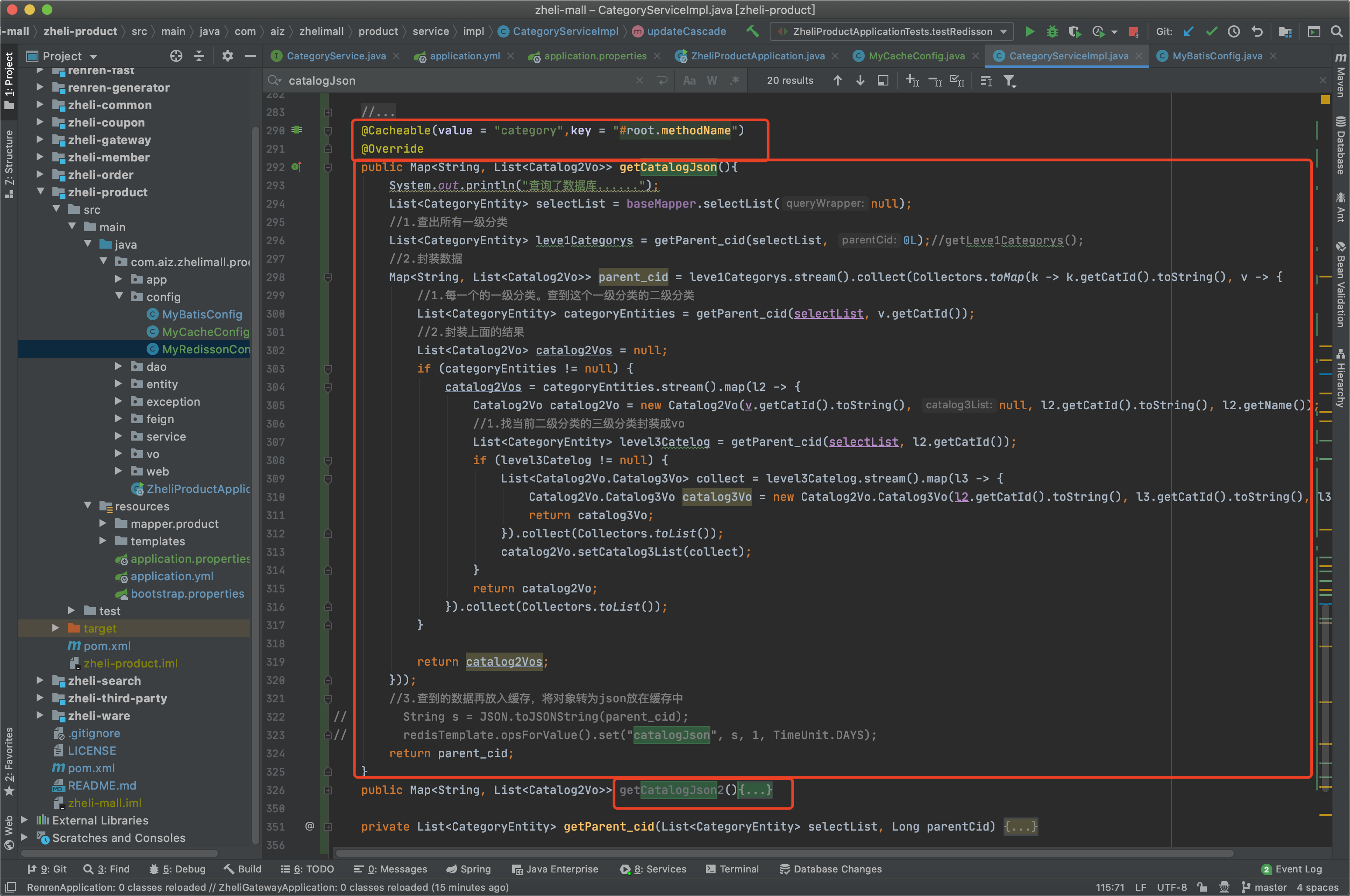
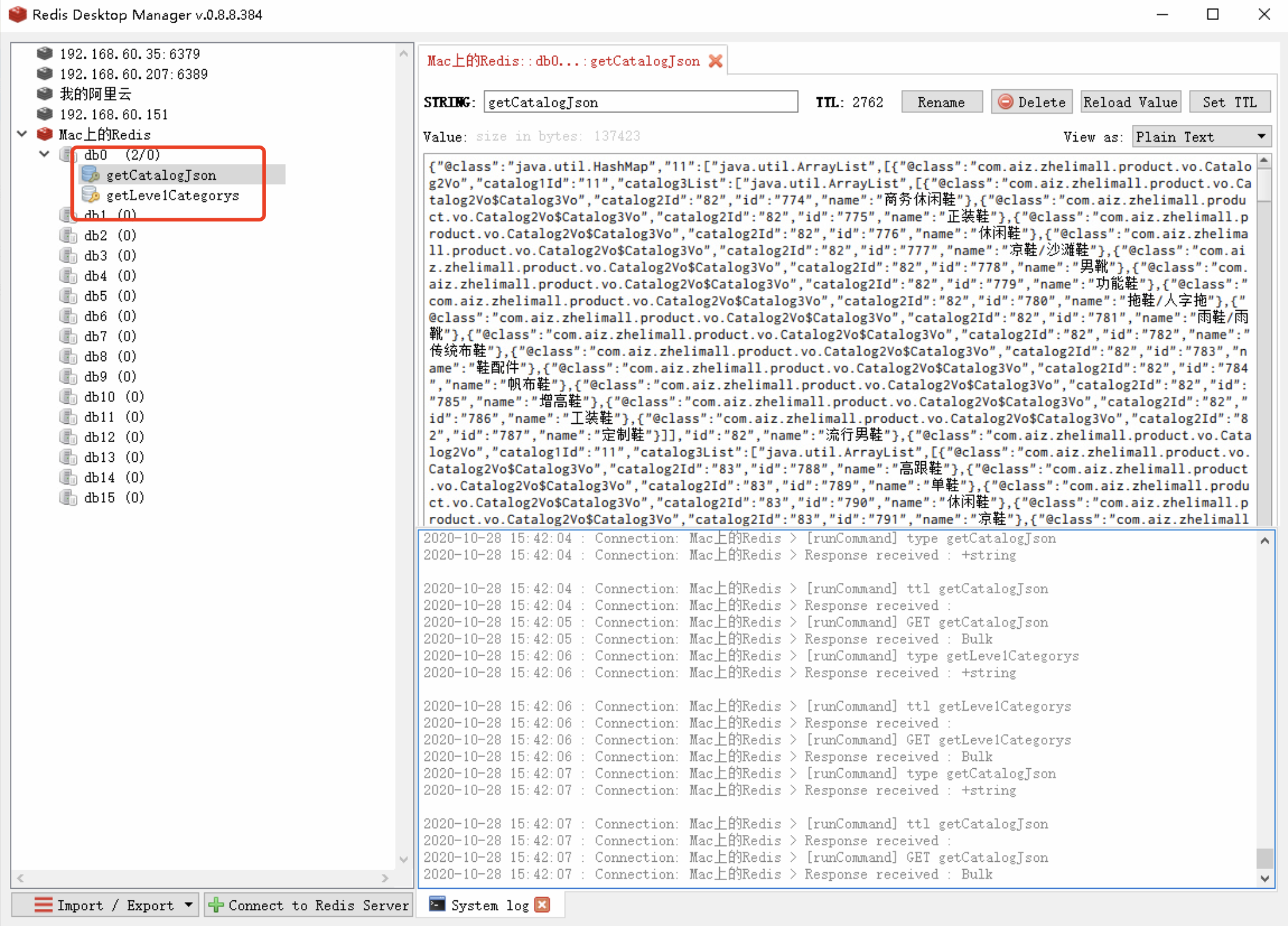
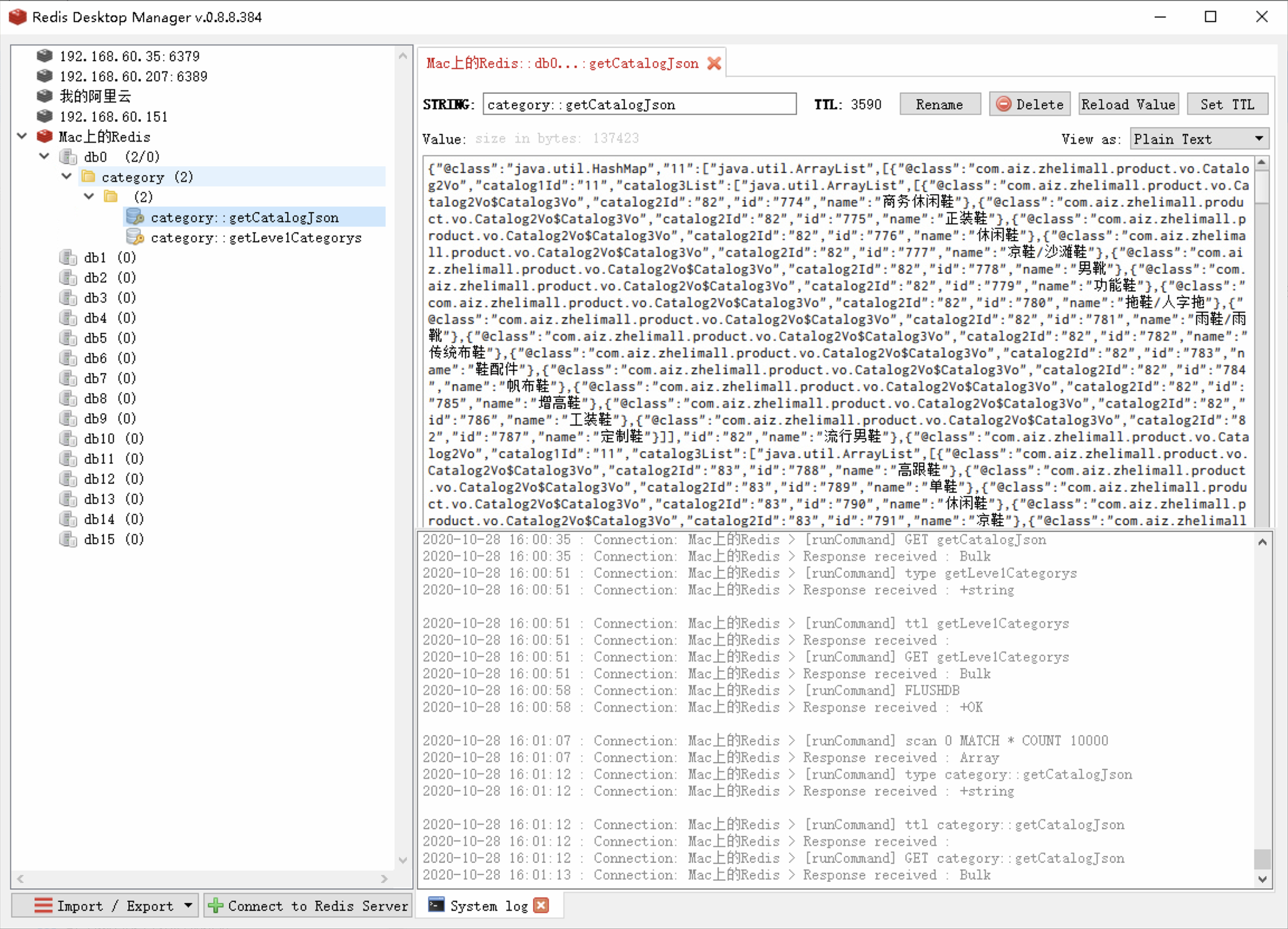
153、缓存-缓存使用-改造三级分类业务 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @Autowired private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;@Override public Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> getCatalogJson(){ String catalogJson = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("catalogJson" ); if (StringUtils.isEmpty(catalogJson)){ Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> catelogJsonFromDb = getCatalogJsonFromDb(); String s = JSON.toJSONString(catelogJsonFromDb); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("catalogJson" ,s); } Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> result = JSON.parseObject(catalogJson,new TypeReference<Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>>>(){}); return result; }
154、缓存-缓存使用-压力测试出的内存泄露及解决
1.springboot2.0以后默认使用lettuce作为操作redis的客户端。它使用netty进行网络通信。
2.lettuce的bug导致netty堆外内存溢出-Xmx300m:netty如果没有指定堆外内存,默认使用-Xmx300m
解决方案:可以通过-Dio.netty.maxDirectMemory只去调大堆外内存。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId > <exclusions > <exclusion > <groupId > io.lettuce</groupId > <artifactId > lettuce-core</artifactId > </exclusion > </exclusions > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > redis.clients</groupId > <artifactId > jedis</artifactId > </dependency >
redisTemplate:
缓存-缓存使用-缓存击穿、穿透、雪崩 缓存穿透 : 指查询一个一定不存在的数据,由于缓存是不命中,将去查询数据库,但是 数据库也无此记录,我们没有将这次查询的null写入缓存,这将导致这个不 存在的数据每次请求都要到存储层去查询,失去了缓存的意义
风险 : 利用不存在的数据进行攻击,数据库瞬时压力增大,最终导致崩溃
解决 : null结果缓存,并加入短暂过期时间
缓存雪崩 : 缓存雪崩是指在我们设置缓存时key采用了相同的过期时间, 导致缓存在某一时刻同时失效,请求全部转发到DB,DB瞬时 压力过重雪崩。解决 : 原有的失效时间基础上增加一个随机值,比如1-5分钟随机,这 样每一个缓存的过期时间的重复率就会降低,就很难引发集体 失效的事件。
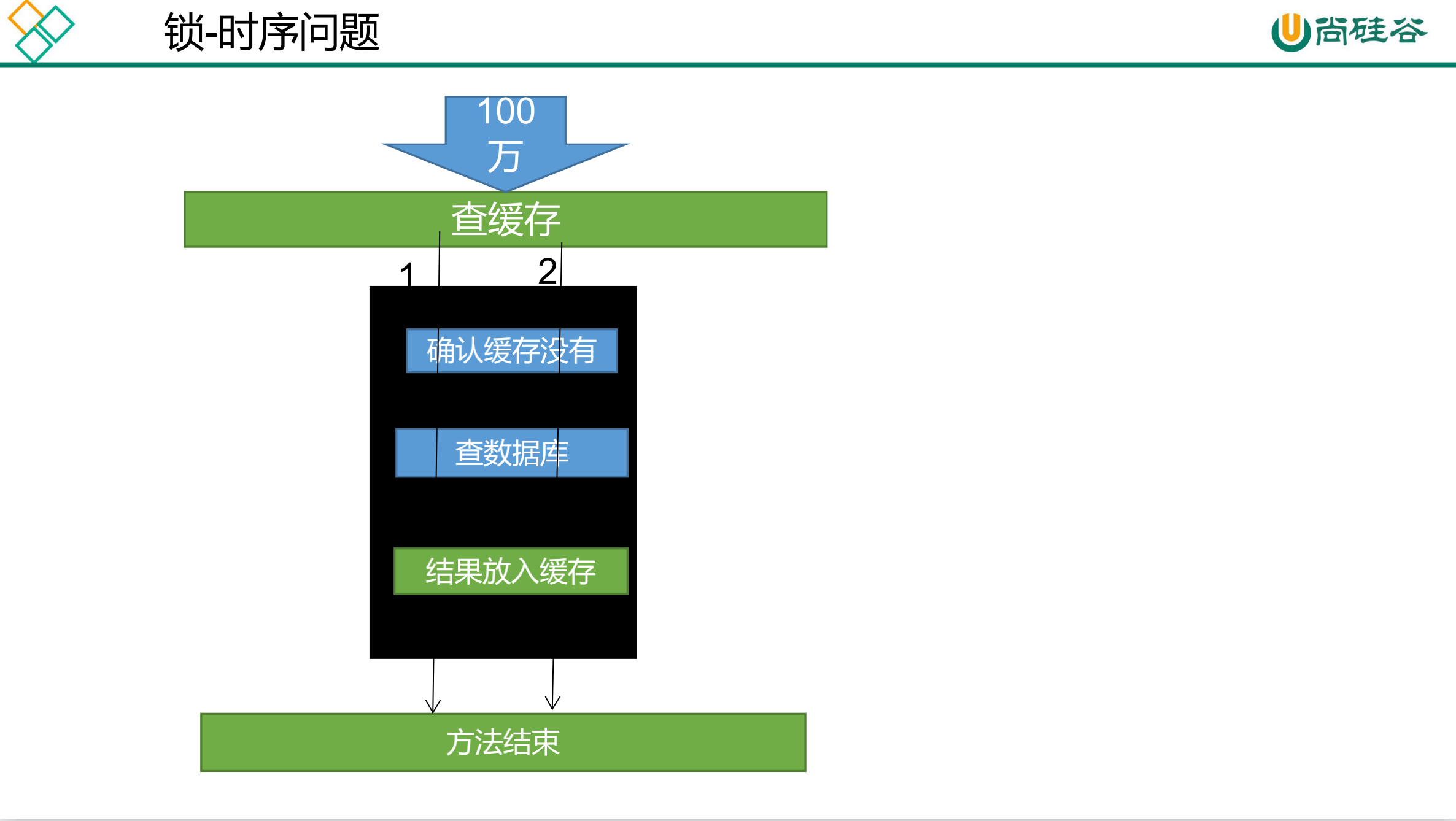
缓存穿透 : 对于一些设置了过期时间的key,如果这些key可能会在某些 时间点被超高并发地访问,是一种非常“热点”的数据。如果这个key在大量请求同时进来前正好失效,那么所有对 这个key的数据查询都落到db,我们称为缓存击穿。解决 : 加锁大量并发只让一个去查,其他人等待,查到以后释放锁,其他 人获取到锁,先查缓存,就会有数据,不用去db
数据穿透:查询一个不存在的数据。缓存null。
数据雪崩:大面积数据同时失效。设置随机过期时间。
数据击穿:大量请求时正好失效。加锁。
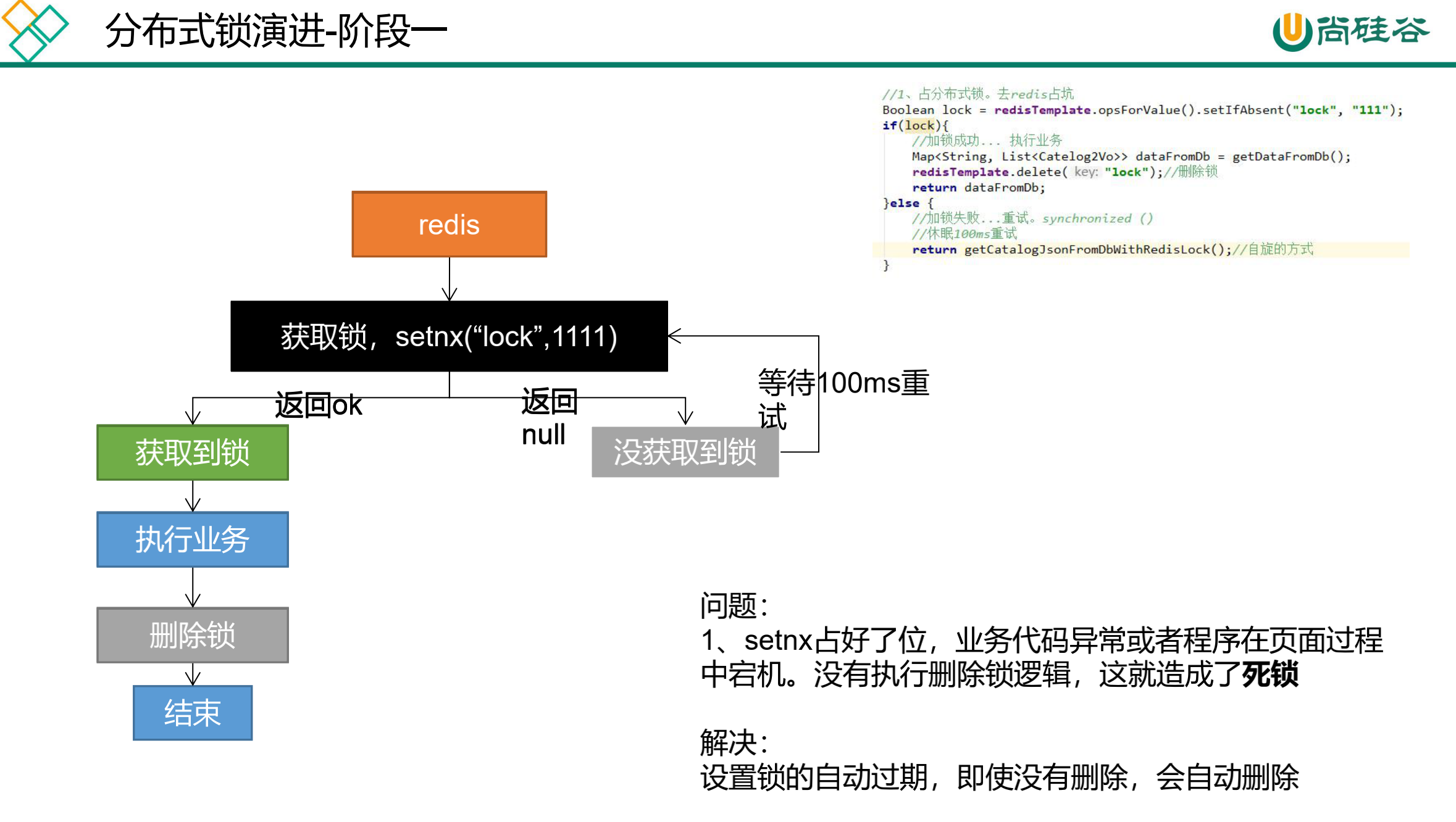
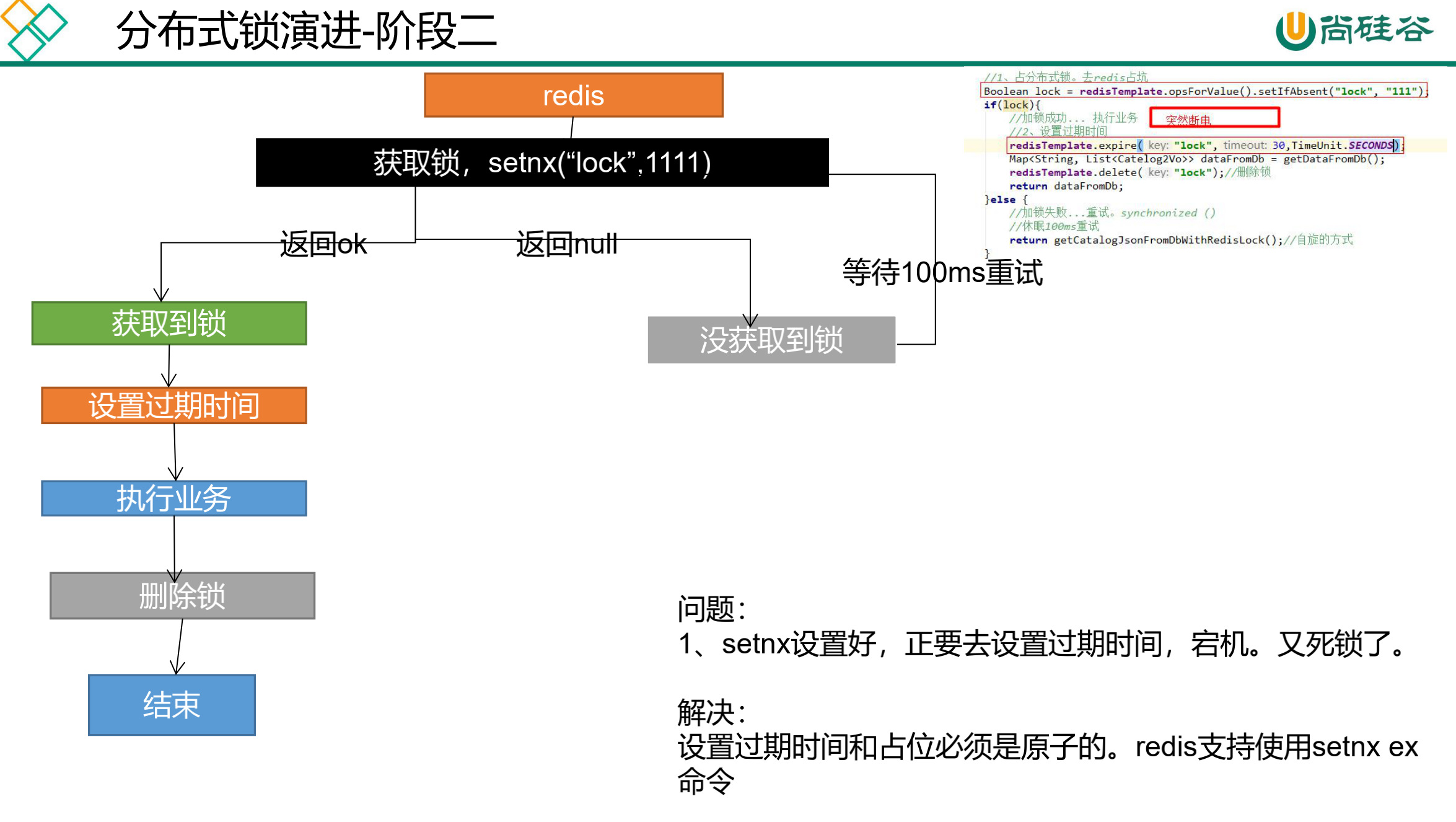
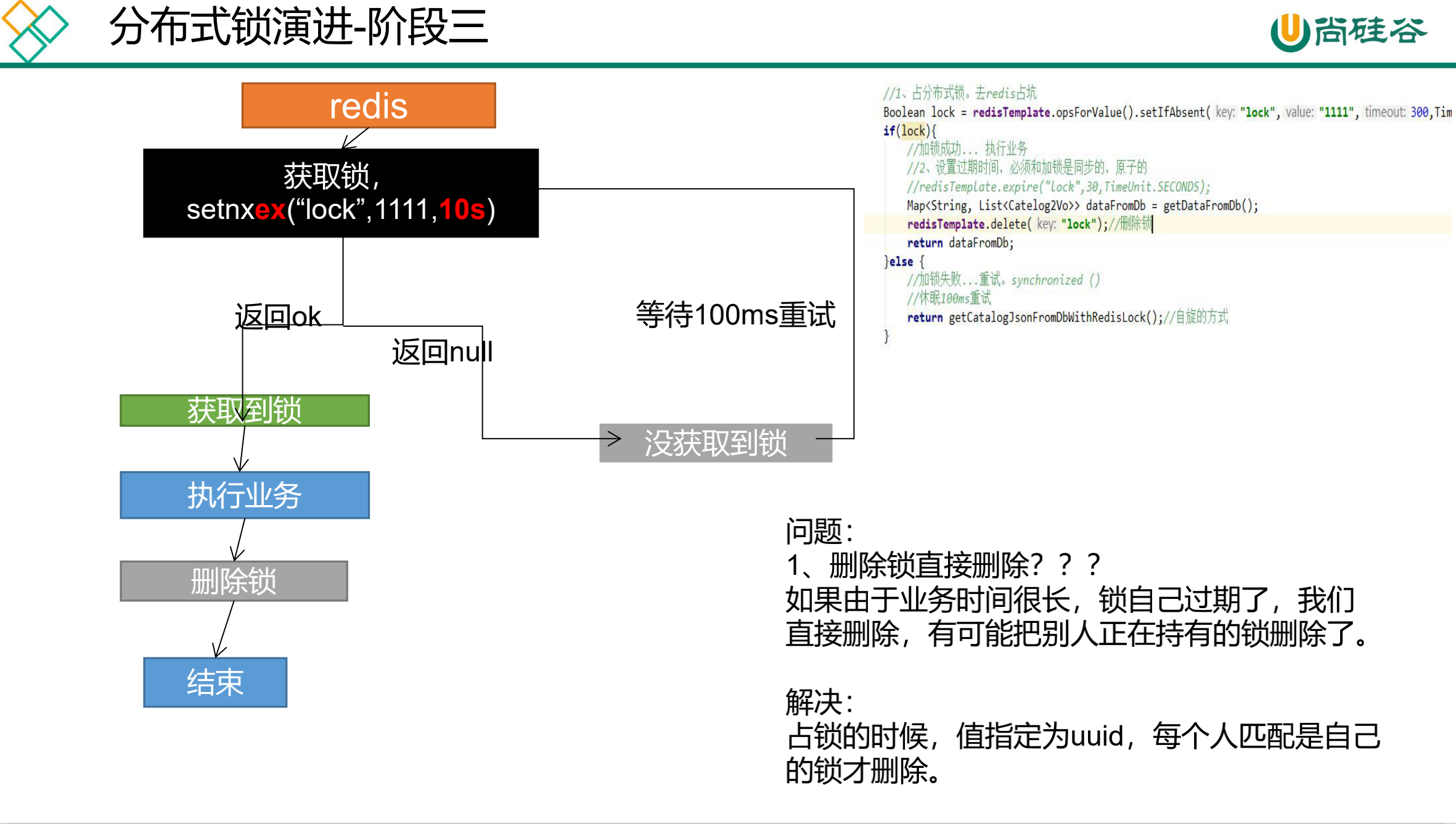
缓存-缓存使用-加锁解决缓存击穿问题 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 @Override public Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> getCatalogJson(){ String catalogJson = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("catalogJson" ); if (StringUtils.isEmpty(catalogJson)){ System.out.println("缓存不命中,将要查询数据库......" ); Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> catelogJsonFromDb = getCatalogJsonFromDb(); return catelogJsonFromDb; } System.out.println("缓存命中,直接返回......" ); Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> result = JSON.parseObject(catalogJson,new TypeReference<Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>>>(){}); return result; } public Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> getCatalogJsonFromDb() { synchronized (this ){ String catalogJson = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("catalogJson" ); if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(catalogJson)){ Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> result = JSON.parseObject(catalogJson,new TypeReference<Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>>>(){}); return result; } System.out.println("查询了数据库......" ); List<CategoryEntity> selectList = baseMapper.selectList(null ); List<CategoryEntity> leve1Categorys = getParent_cid(selectList,0L ); Map<String, List<Catalog2Vo>> parent_cid = leve1Categorys.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(k -> k.getCatId().toString(), v -> { List<CategoryEntity> categoryEntities = getParent_cid(selectList,v.getCatId()); List<Catalog2Vo> catalog2Vos = null ; if (categoryEntities != null ) { catalog2Vos = categoryEntities.stream().map(l2 -> { Catalog2Vo catalog2Vo = new Catalog2Vo(v.getCatId().toString(), null , l2.getCatId().toString(), l2.getName()); List<CategoryEntity> level3Catelog = getParent_cid(selectList,l2.getCatId()); if (level3Catelog!=null ){ List<Catalog2Vo.Catalog3Vo> collect = level3Catelog.stream().map(l3 -> { Catalog2Vo.Catalog3Vo catalog3Vo = new Catalog2Vo.Catalog3Vo(l2.getCatId().toString(), l3.getCatId().toString(), l3.getName()); return catalog3Vo; }).collect(Collectors.toList()); catalog2Vo.setCatalog3List(collect); } return catalog2Vo; }).collect(Collectors.toList()); } return catalog2Vos; })); String s = JSON.toJSONString(parent_cid); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("catalogJson" ,s,1 , TimeUnit.DAYS); return parent_cid; } }
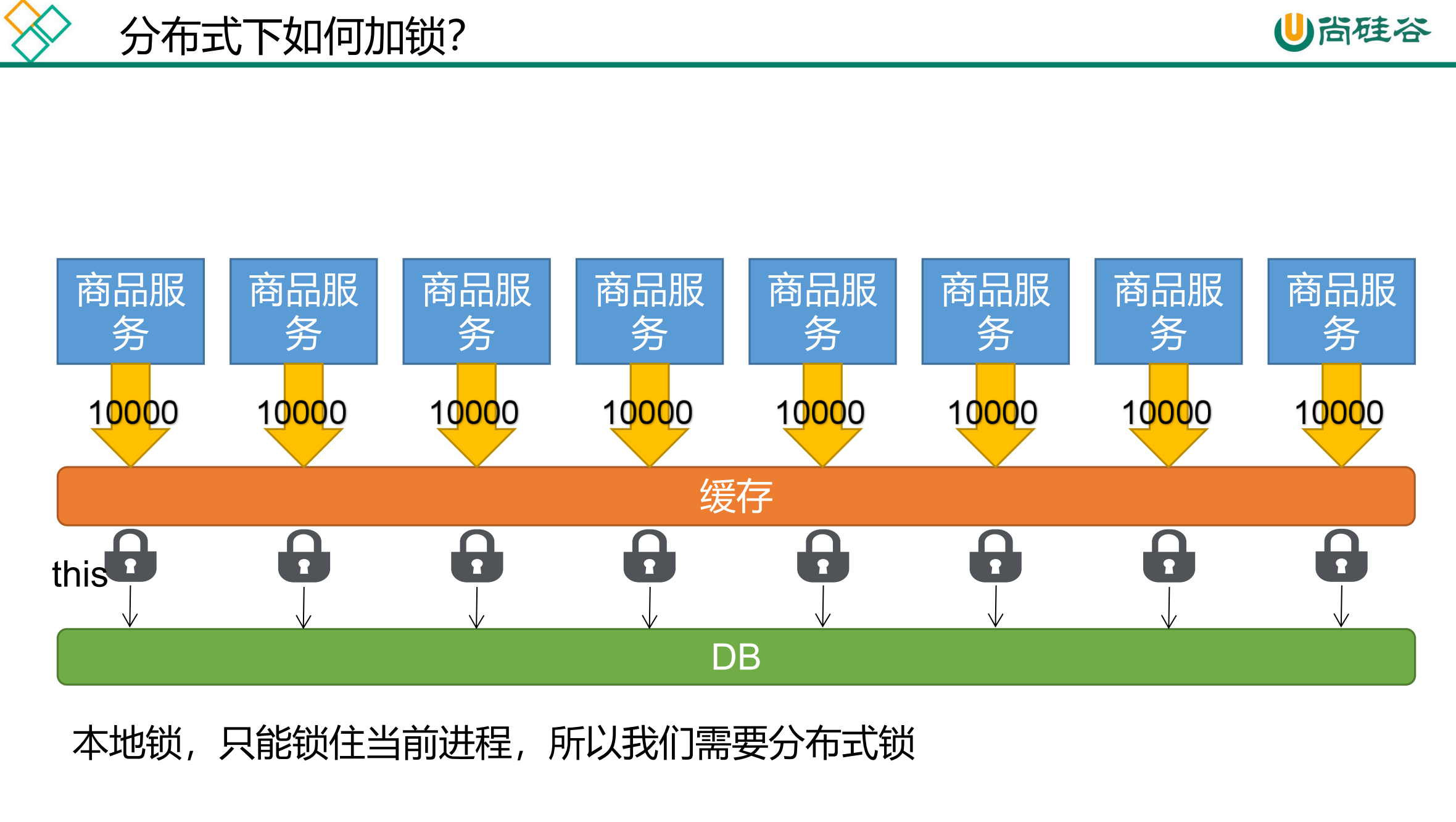
157、缓存-缓存使用-本地锁在分布式下的问题
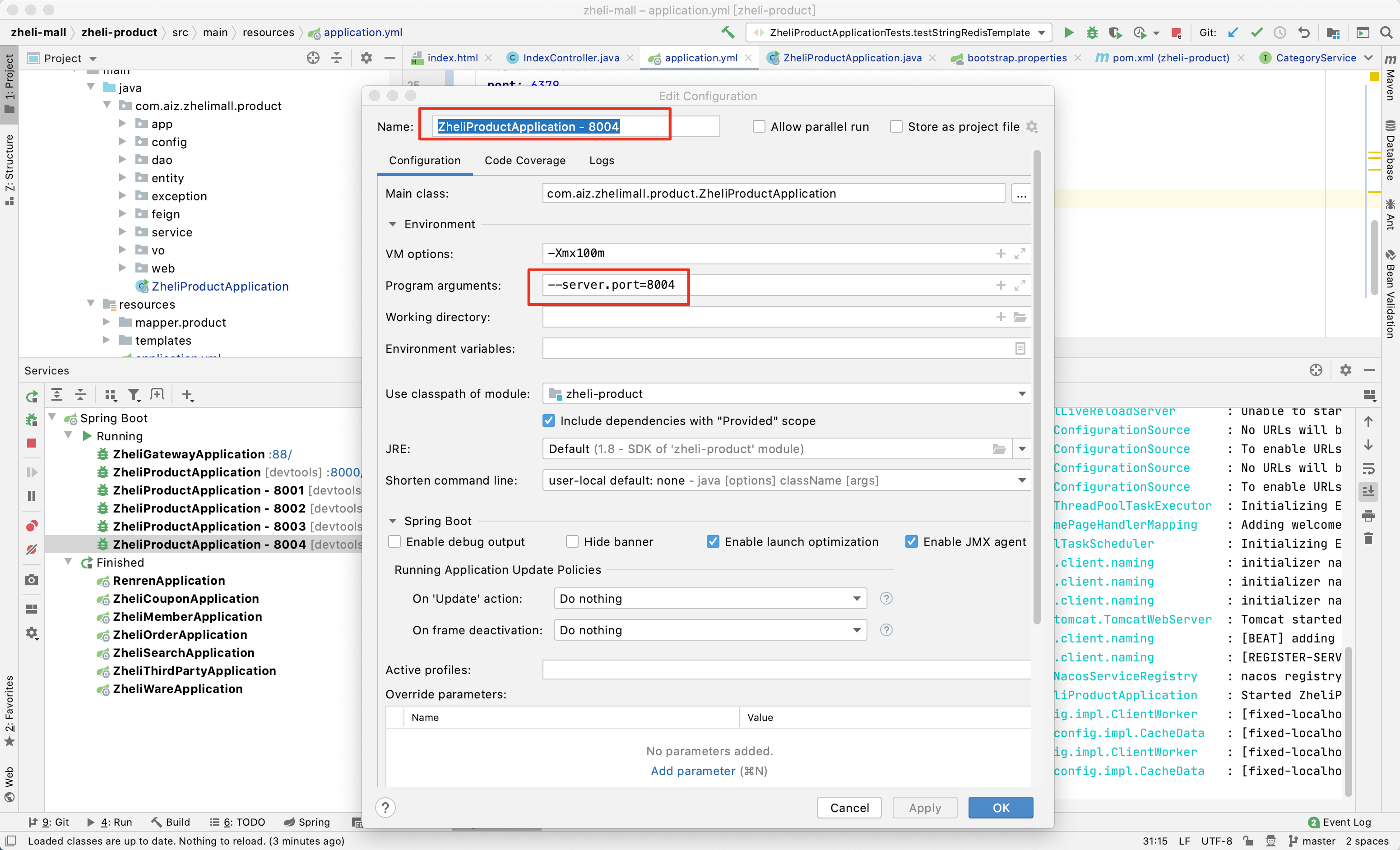
首先需要在idea中启动多个springboot实例。右击Services中的ZheliProductApplication,然后选择Copy Configuration。然后设置参数,Name修改为可以分辨出的就可以,Product arguments修改为--server.port=8004。
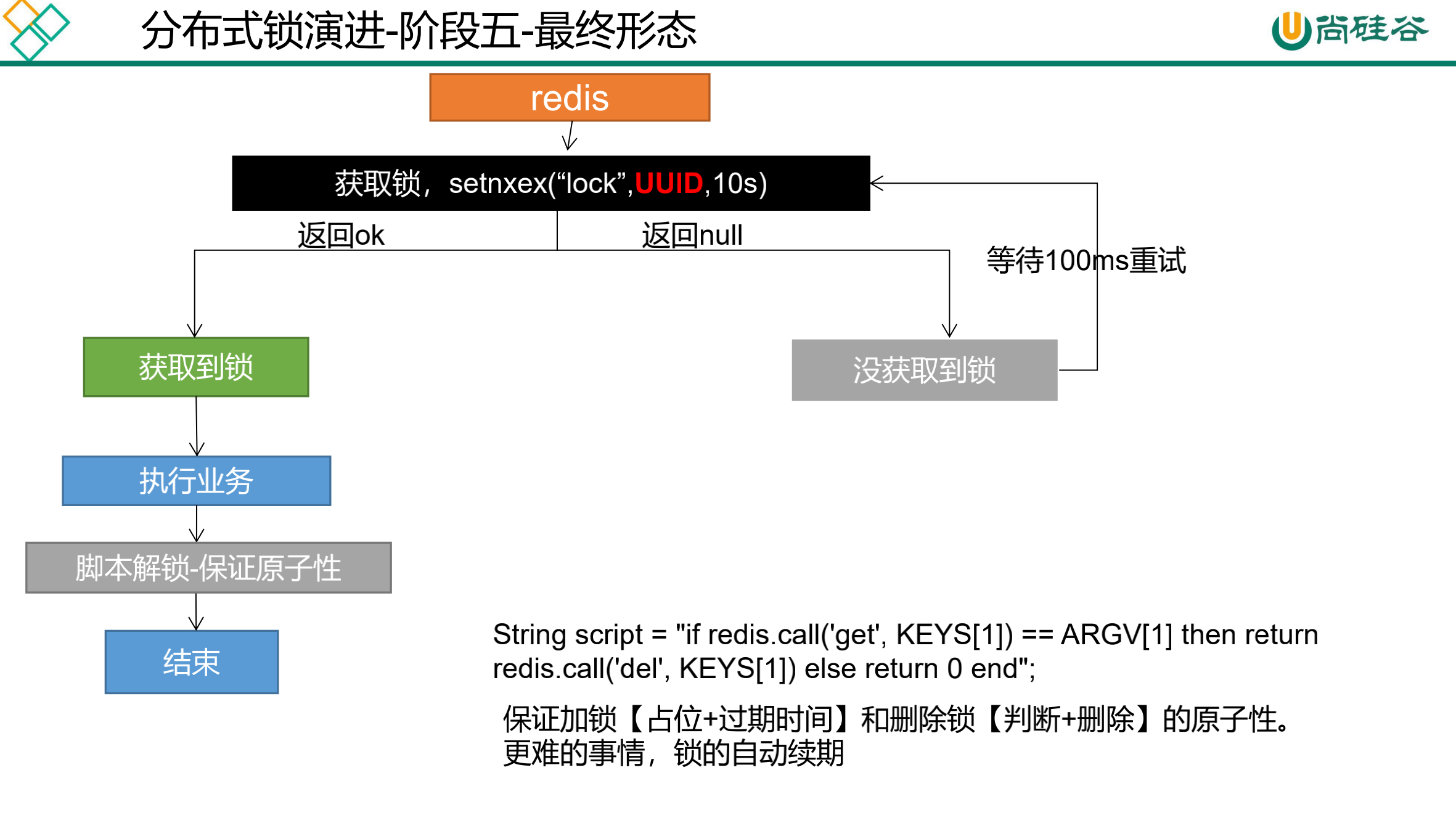
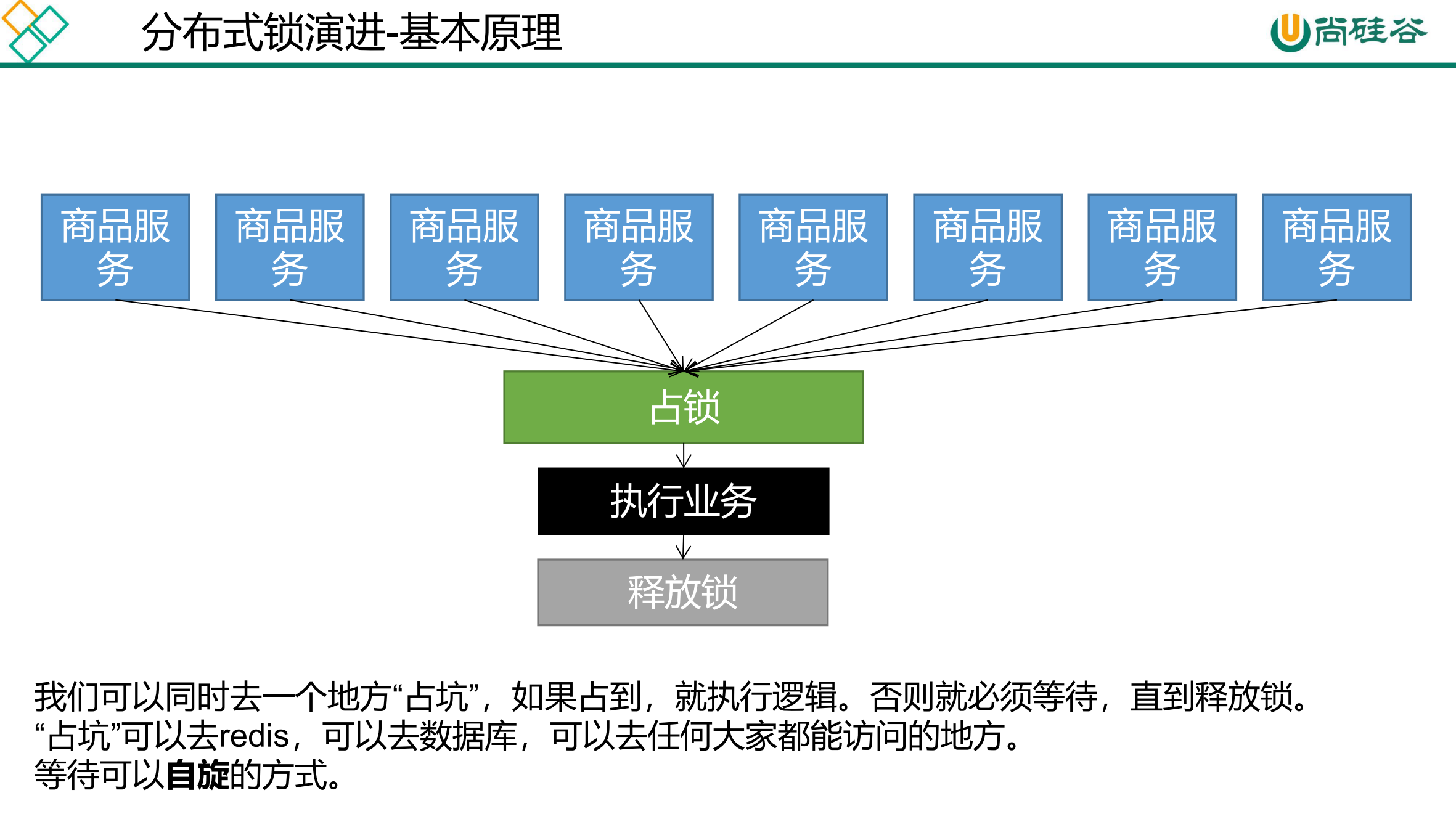
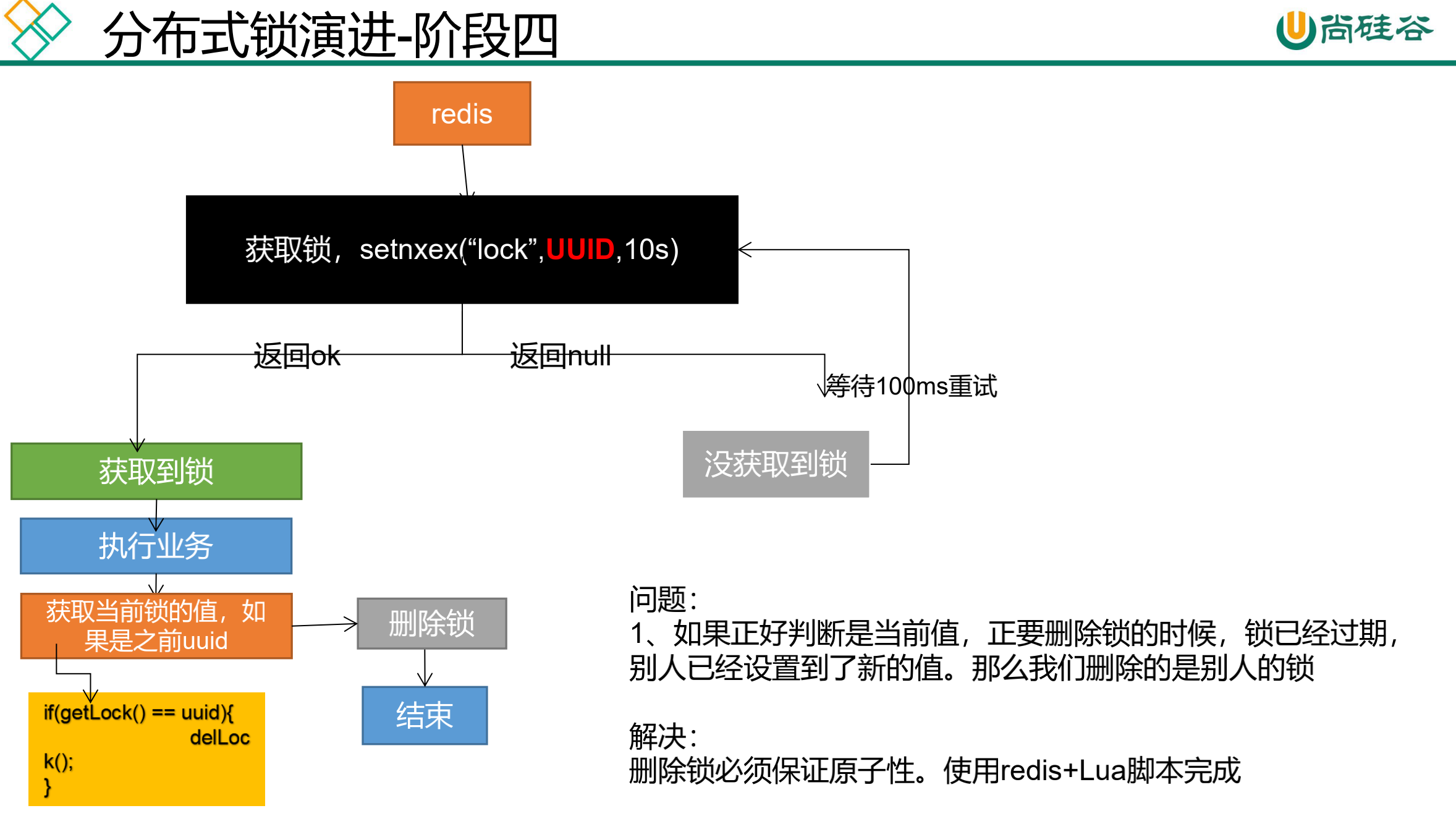
缓存-分布式锁-分布式锁原理与使用
我们这边的分布式锁使用redis的setnx实现;http://www.redis.cn/commands/set.html
缓存-分布式锁-Redisson简介&整合 https://redis.io/topics/distlock
https://github.com/redisson/redisson/wiki/Table-of-Content
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.redisson/redisson
整合redisson作为分布式锁等功能框架 (一).引入依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.redisson/redisson --> <dependency> <groupId>org.redisson</groupId> <artifactId>redisson</artifactId> <version>3.12.0</version> </dependency>
(二).配置redisson
https://github.com/redisson/redisson/wiki/2.-%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE%E6%96%B9%E6%B3%95
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Configuration public class MyRedissonConfig @Bean (destroyMethod="shutdown" ) RedissonClient redisson () throws IOException { Config config = new Config(); config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379" ); RedissonClient redissonClient = Redisson.create(config); return redissonClient; } }
测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Slf 4j@SpringBootTest class ZheliProductApplicationTests @Autowired private RedissonClient redissonClient; @Test public void testRedisson () System.out.println(redissonClient); } }
160、缓存-分布式锁-Redisson-lock锁测试 161、缓存-分布式锁-Redisson-lock看门狗原理-redisson如何解决死锁 可重入锁(Reentrant Lock) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 @ResponseBody @GetMapping ("/hello" )public String hello () RLock lock = redisson.getLock("my-lock" ); lock.lock(10 , TimeUnit.SECONDS); try { System.out.println("加锁成功,执行业务......" +Thread.currentThread().getId()); Thread.sleep(30 *1000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } finally { System.out.println("释放锁......" +Thread.currentThread().getId()); lock.unlock(); } return "Hello" ; }
打开浏览器两个窗口同时访问http://localhost:8000/hello。会发现同时只有一个线线程会获取锁对象。控制台信息打印如下。
1 2 3 4 加锁成功,执行业务......424 释放锁......424 加锁成功,执行业务......426 释放锁......426
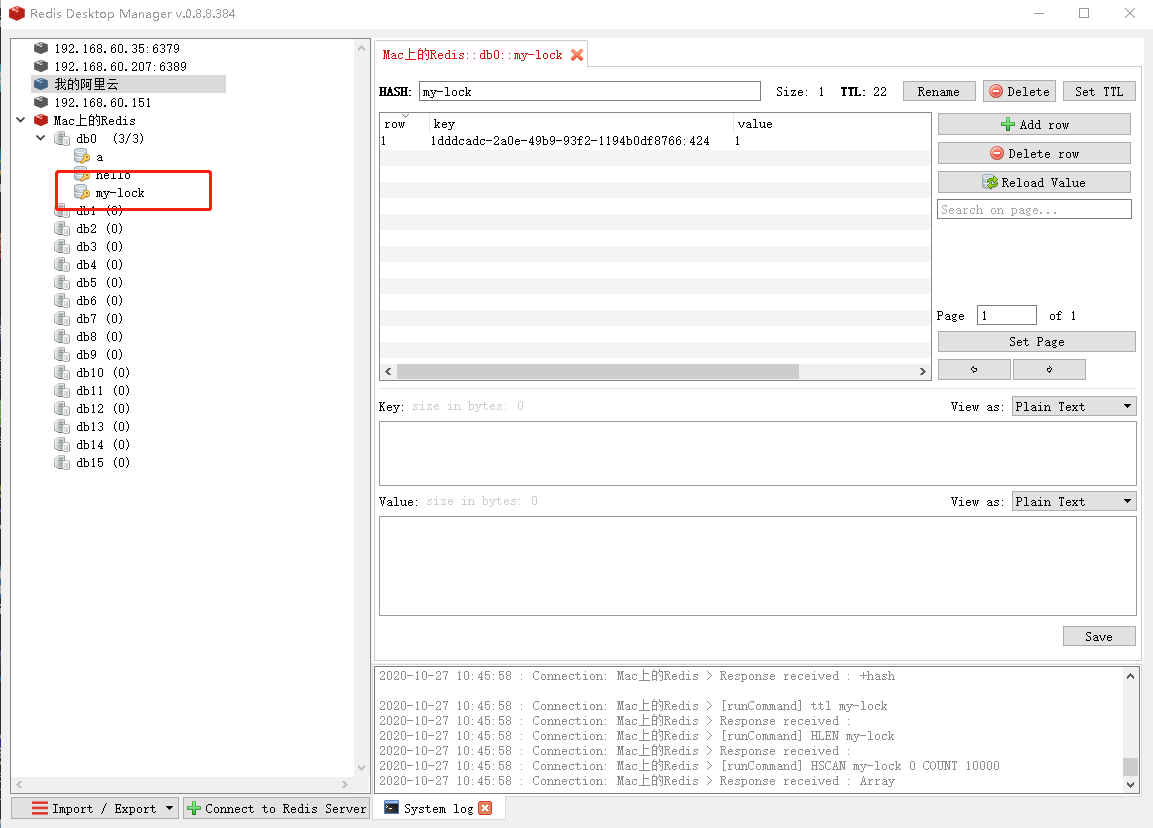
运行过程中,Redis中的状态。当运行完毕后或者超时my-lock数据会过期。
162、缓存-分布式锁-Redisson-读写锁测试 163、缓存-分布式锁-Redisson-读写锁补充 读写锁(ReadWriteLock) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 @ResponseBody @GetMapping ("/write" )public String writeValue () RReadWriteLock lock = redisson.getReadWriteLock("rw-lock" ); RLock rLock = lock.writeLock(); String s = "" ; try { rLock.lock(); System.out.println("写锁加锁成功..." +Thread.currentThread().getId()); s = UUID.randomUUID().toString(); Thread.sleep(30 *1000 ); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("writeValue" ,s); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { rLock.unlock(); System.out.println("写锁释放..." +Thread.currentThread().getId()); } return s; } @ResponseBody @GetMapping ("/read" )public String readValue () RReadWriteLock lock = redisson.getReadWriteLock("rw-lock" ); System.out.println("读锁加锁成功..." +Thread.currentThread().getId()); String s = "" ; RLock rLock = lock.readLock(); rLock.lock(); try { s = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("writeValue" ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { rLock.unlock(); System.out.println("读锁释放..." +Thread.currentThread().getId()); } return s; }
164、缓存-分布式锁-Redisson-信号量测试 信号量(Semaphore) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 @ResponseBody @GetMapping ("/park" )public String park () throws InterruptedException RSemaphore park = redisson.getSemaphore("park" ); boolean b = park.tryAcquire(); if (b){ }else { return "error" ; } return "ok=>" +b; } @ResponseBody @GetMapping ("/go" )public String go () throws InterruptedException RSemaphore park = redisson.getSemaphore("park" ); park.release(); return "ok" ; }
165、缓存-分布式锁-Redisson-闭锁测试 闭锁(CountDownLatch) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 @ResponseBody @GetMapping ("/lockDoor" )public String lockDoor () throws InterruptedException RCountDownLatch door = redisson.getCountDownLatch("door" ); door.await(); return "放假了..." ; } @ResponseBody @GetMapping ("/gogogo/{id}" )public String gogogog (@PathVariable("id" ) Long id) RCountDownLatch door = redisson.getCountDownLatch("door" ); door.countDown(); return id+"班的人都走了..." ; }
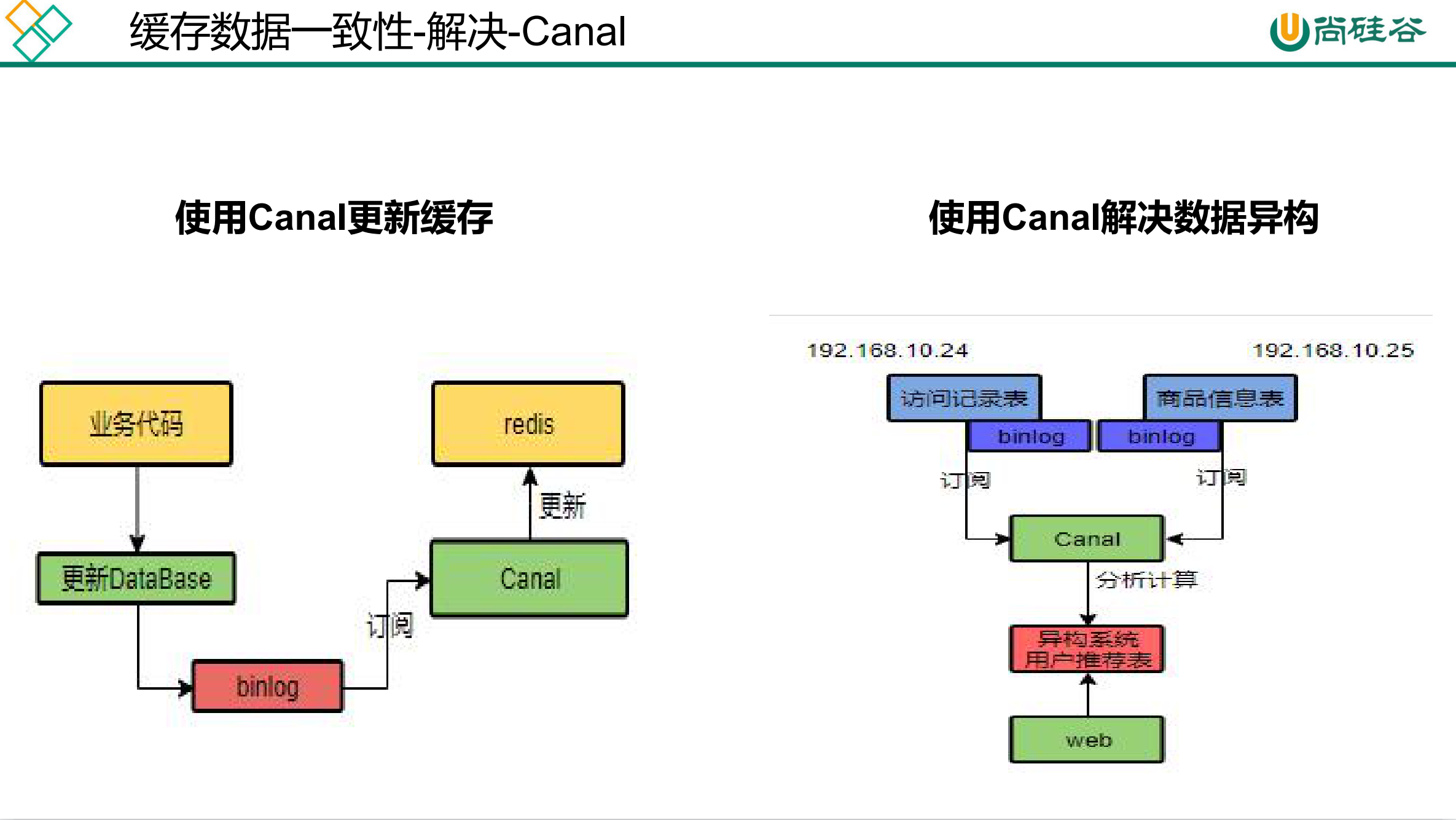
166、缓存-分布式锁-缓存一致性解决
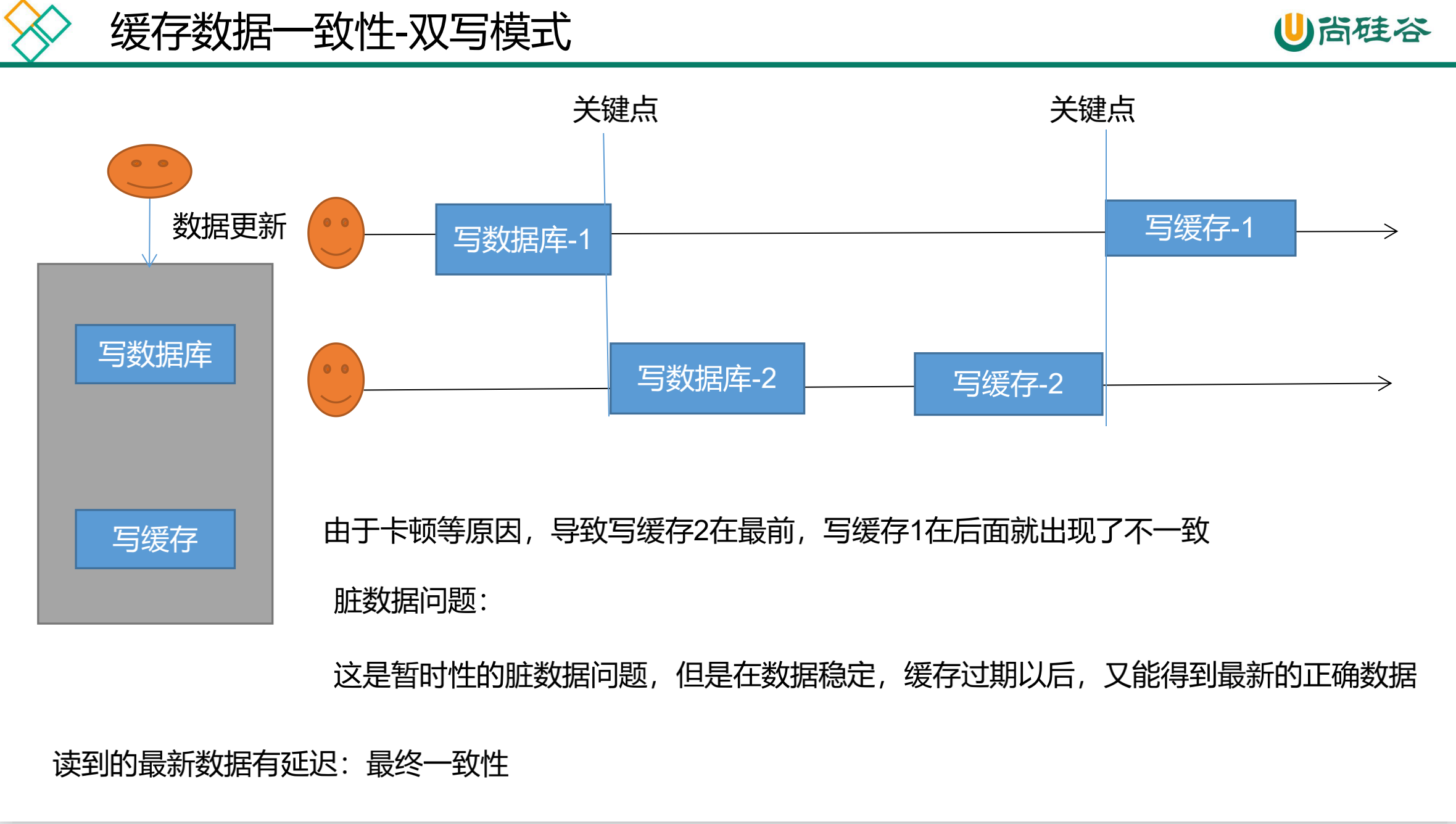
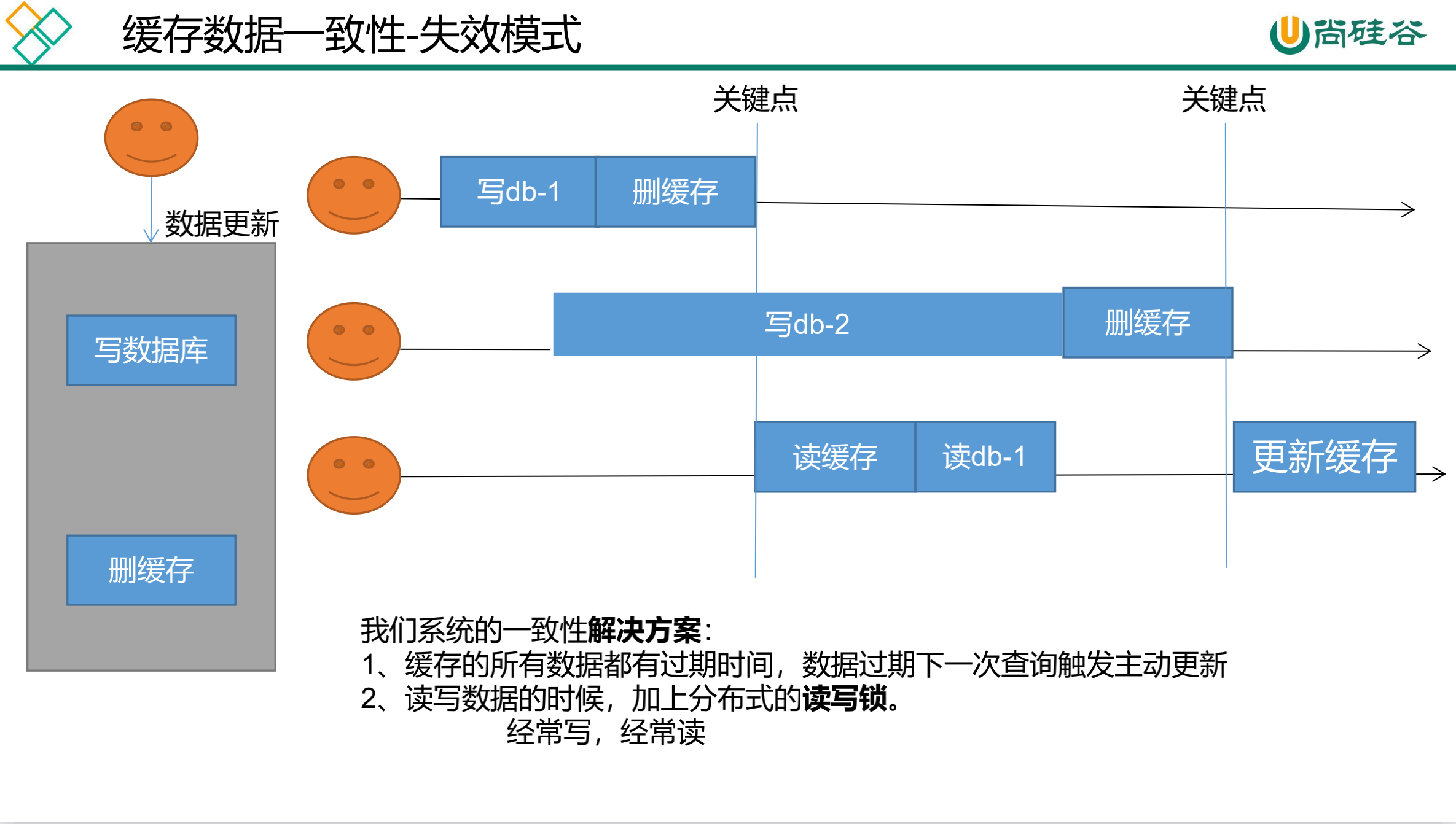
无论是双写模式还是失效模式,都会导致缓存的不一致问题。即多个实例同时更新会出事。怎么办?
如果是用户纬度数据(订单数据、用户数据),这种并发几率非常小,不用考虑这个问题,缓存数据加上过期时间,每隔一段时间触发读的主动更新即可。
如果是菜单,商品介绍等基础数据,也可以去使用canal订阅binlog的方式。
缓存数据+过期时间也足够解决大部分业务对于缓存的要求。
通过加锁保证并发读写,写写的时候按顺序排好队。读读无所谓。所以适合使用读写锁。(业务不关心脏数据,允许临时脏数据可忽略);
总结:
我们能放入缓存的数据本就不应该是实时性、一致性要求超高的。所以缓存数据的时候加上过期时间,保 证每天拿到当前最新数据即可。
我们不应该过度设计,增加系统的复杂性。
遇到实时性、一致性要求高的数据,就应该查数据库,即使慢点。
167、缓存-SpringCache-简介
168、缓存-SpringCache-整合&体验@Cacheable 整合SpringCache简化缓存开发
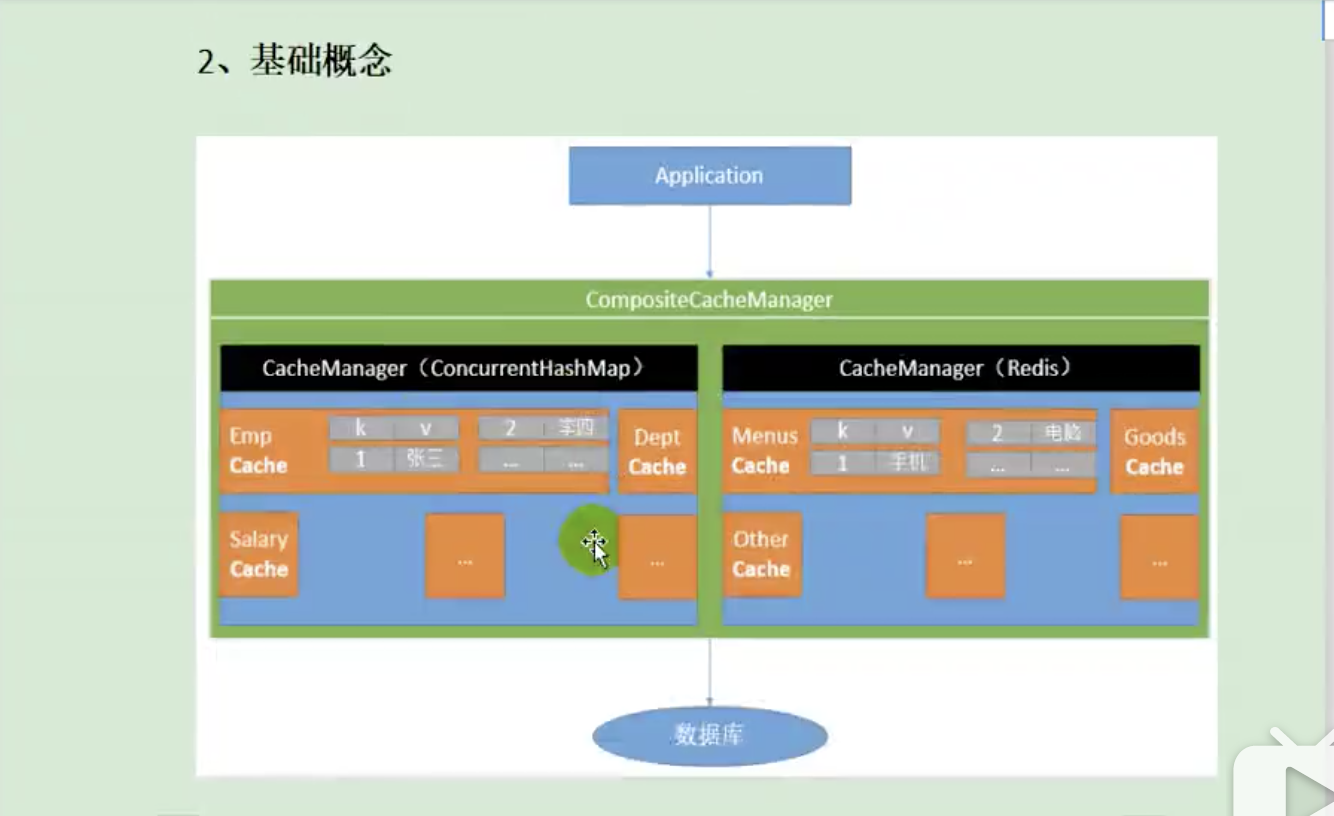
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 (一).引入依赖 spring-boot-starter-cache、spring-boot-starter-data-redis (二).写配置 (1).自动配置了哪些? CacheAutoConfiguration会导入RedisCacheConfiguration 自动配置好了缓存管理器RedisCacheManager (2).配置使用redis作为缓存 在application.properties中配置。 (3).测试使用缓存 @Cacheable: Triggers cache population.触发将数据保存到缓存的操作 @CacheEvict: Triggers cache eviction.触发将数据从缓存删除的操作 @CachePut: Updates the cache without interfering with the method execution.不影响方法执行更新缓存 @Caching: Regroups multiple cache operations to be applied on a method.组合以上多个操作 @CacheConfig: Shares some common cache-related settings at class-level.在类级别共享缓存的相同配置 (1).开启缓存功能@EnableCaching (2).只需要使用注解就能完成缓存操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId > <version > 2.3.4.RELEASE</version > </dependency >
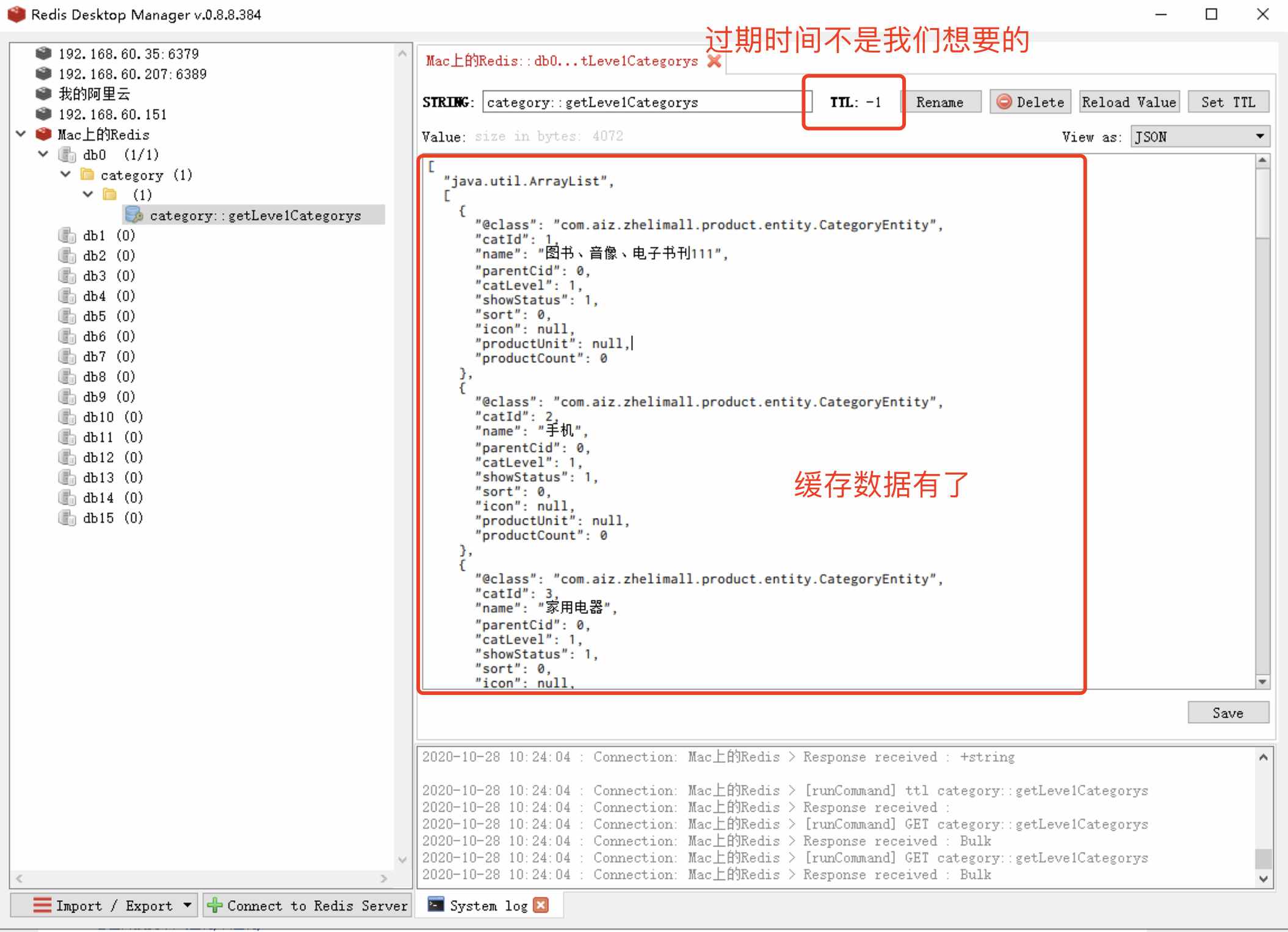
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Cacheable ({"category" }) @Override public List<CategoryEntity> getLeve1Categorys () List<CategoryEntity> categoryEntities = baseMapper.selectList(new QueryWrapper<CategoryEntity>().eq("parent_cid" , 0 )); return categoryEntities; }
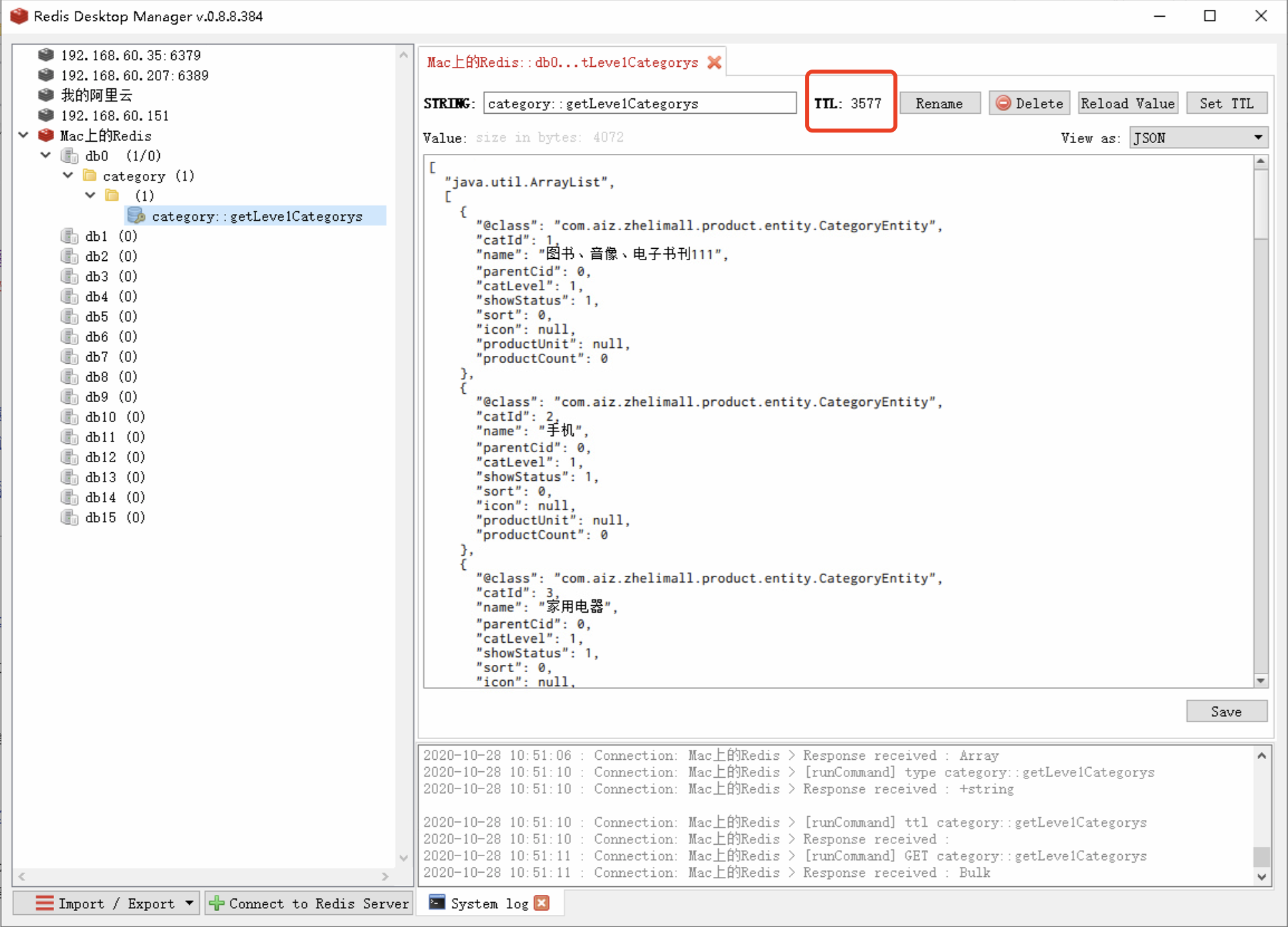
运行加了@Cacheable注解的方法,可以在redis中查看缓存数据。
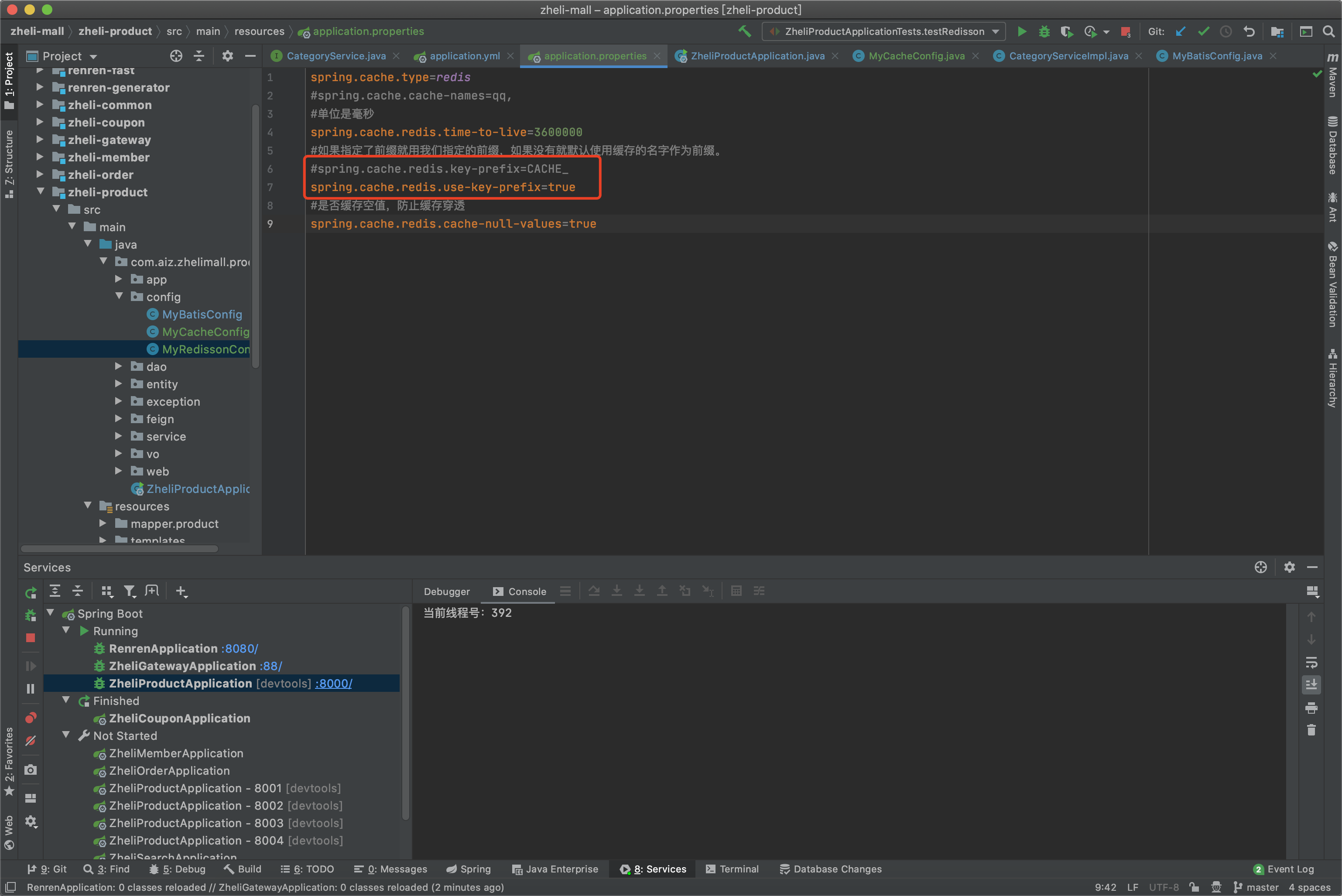
169、缓存-SpringCache-@Cacheable细节设置 1 2 spring.cache.redis.time-to-live =3600000
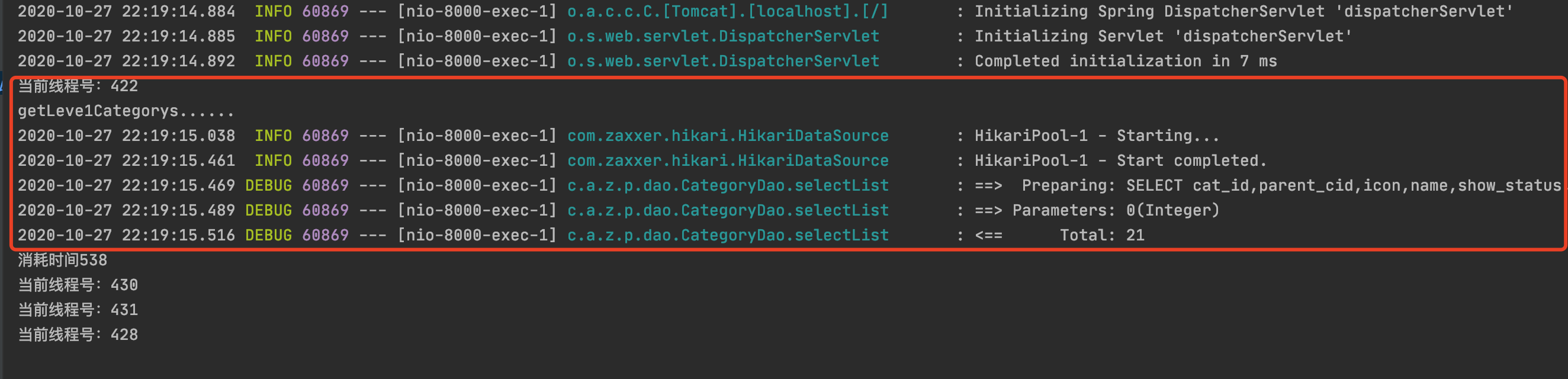
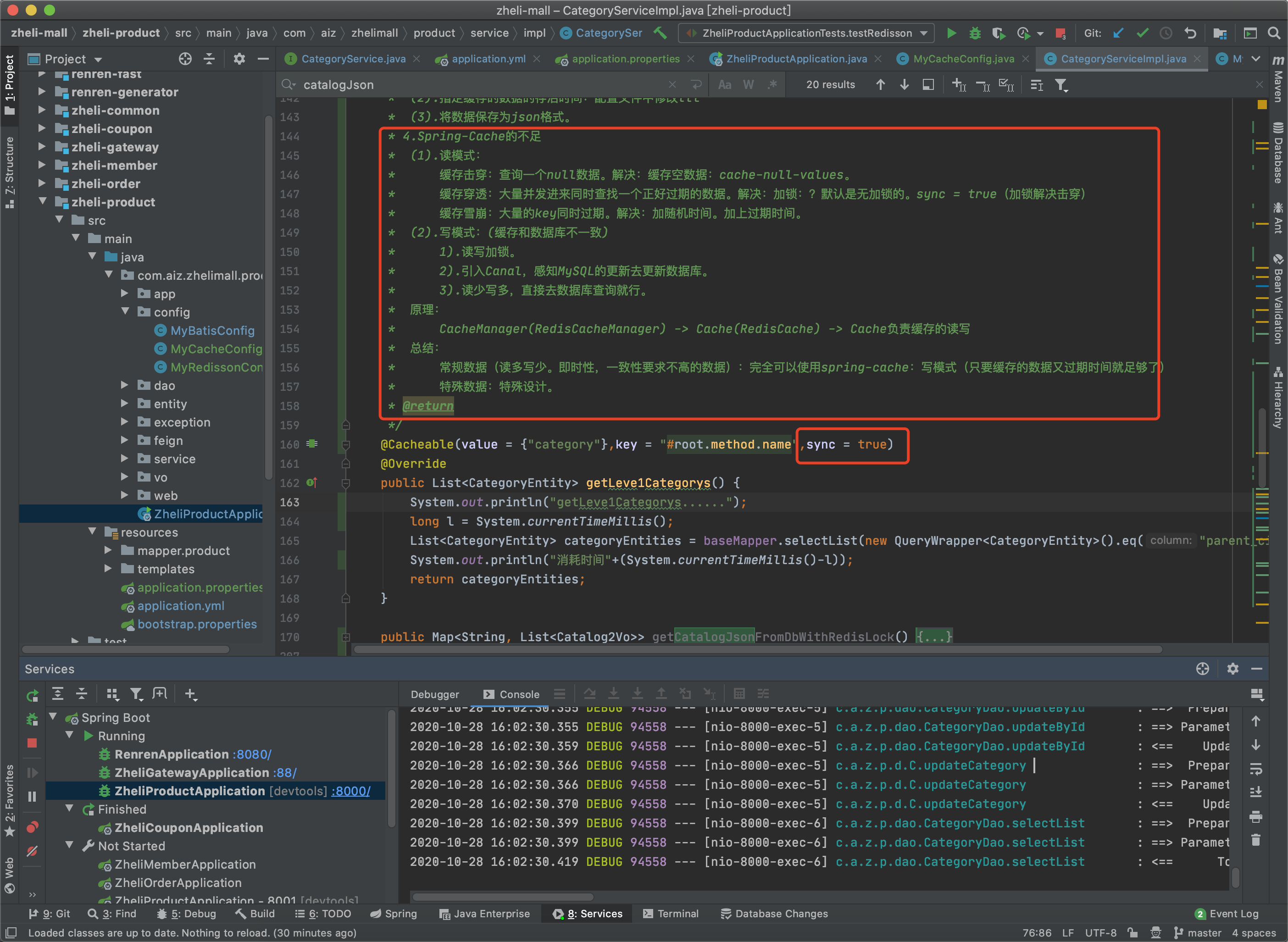
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Cacheable (value = {"category" },key = "#root.method.name" )@Override public List<CategoryEntity> getLeve1Categorys () System.out.println("getLeve1Categorys......" ); long l = System.currentTimeMillis(); List<CategoryEntity> categoryEntities = baseMapper.selectList(new QueryWrapper<CategoryEntity>().eq("parent_cid" , 0 )); System.out.println("消耗时间" +(System.currentTimeMillis()-l)); return categoryEntities; }
SpEL语法:https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/5.3.0-SNAPSHOT/reference/html/integration.html#cache-spel-context
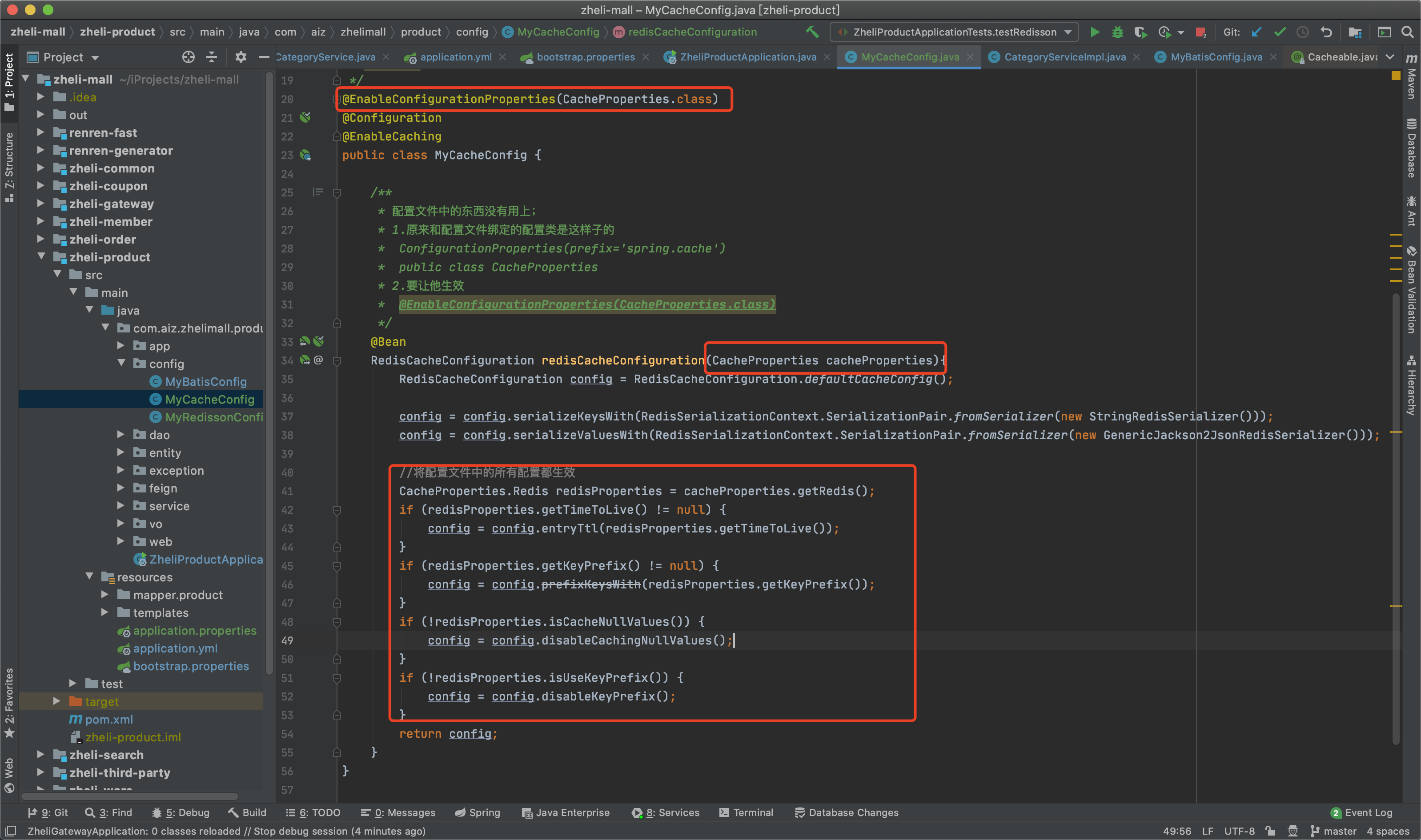
170、缓存-SpringCache-自定义缓存配置 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Configuration @EnableCaching public class MyCacheConfig @Bean RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration () { RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig(); config = config.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer())); config = config.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer())); return config; } }
application.properties里面配置了过期时间,为了使我们的配置生效。
重新启动后,查看redis中的缓存数据。
配置其他内容。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 spring.cache.type =redis spring.cache.redis.time-to-live =3600000 spring.cache.redis.key-prefix =CACHE_ spring.cache.redis.use-key-prefix =false spring.cache.redis.cache-null-values =true
171、缓存-SpringCache-@CacheEvict 缓存失效模式:修改的时候使缓存消失,下次重新查询的时候,再加入缓存。
修改过后就可以在 RedisDeskTopManager客户端查看,可以看到缓存删除了。
之后修改我们原本获取三级分类的方法。
重启服务,刷新首页。
第一次访问之后缓存就存到redis中了,再次刷新首页就不会去访问数据库了。
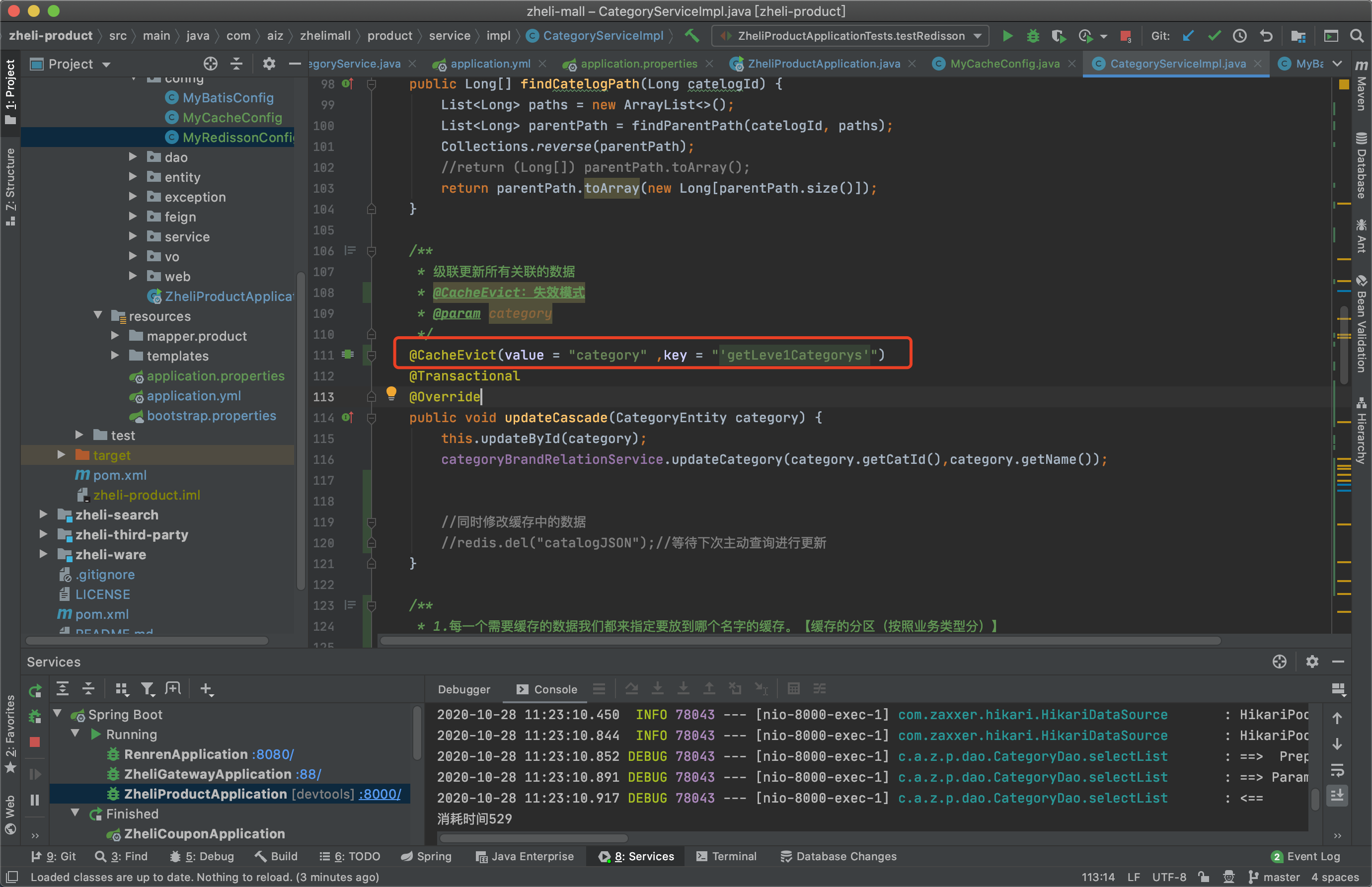
但是现在修改菜单数据之后删除键为getLeve1Categorys的缓存数据,我们想要修改菜单之后两个缓存数据都删除掉。有以下两种方式:
1.同时进行多种缓存:@Caching
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Caching (evict = { @CacheEvict (value = "category" ,key = "'getLeve1Categorys'" ), @CacheEvict (value = "category" ,key = "'getCatalogJson'" ), }) @Transactional @Override public void updateCascade (CategoryEntity category) this .updateById(category); categoryBrandRelationService.updateCategory(category.getCatId(),category.getName()); }
推荐配置
1 2 //@CachePut//双写模式 @CacheEvict(value = "category",allEntries = true)//失效模式
172、缓存-SpringCache-原理与不足 Spring-Cache的不足
读模式:
缓存击穿:查询一个null数据。解决:缓存空数据:cache-null-values。
缓存穿透:大量并发进来同时查找一个正好过期的数据。解决:加锁:?默认是无加锁的。sync = true(加锁解决击穿)
缓存雪崩:大量的key同时过期。解决:加随机时间。加上过期时间。
写模式:(缓存和数据库不一致)
1).读写加锁。
2).引入Canal,感知MySQL的更新去更新数据库。
3).读少写多,直接去数据库查询就行。
原理
CacheManager(RedisCacheManager) -> Cache(RedisCache) -> Cache负责缓存的读写
总结:
常规数据(读多写少。即时性,一致性要求不高的数据):完全可以使用spring-cache:写模式(只要缓存的数据又过期时间就足够了)
特殊数据:特殊设计。